In Silico analysis of Ceruloplasmin alteration in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Keywords:
Oral squamous cell carcinoma, Ceruloplasmin, Insilico analysis, prognostic marker, cancer therapeuticAbstract
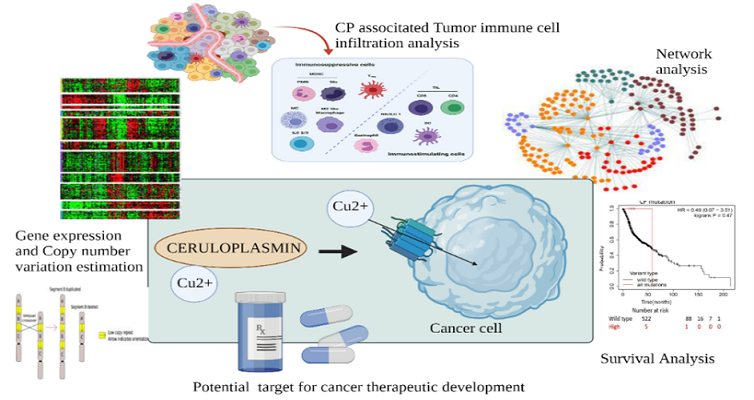
Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC) incidence in India is very high, reaching 37.2 % of all cancer cases diagnosed in the advanced stages, extending a need to explore valuable diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic biomarkers for OSCC. Ceruloplasmin (CP), a multifunctional molecule involved in iron metabolism and copper transport, has been found to be upregulated in multiple tumor types, however its expression profile and prognostic potential, in OSCC remains unexplored. Using in silico analysis approach, we found Ceruloplasmin mRNA and protein expression greatly increased in high-grade oral cancer patients, suggesting ceruloplasmin could be a potential prognostic marker for late stage OSCC. On integration of gene expression profiles, molecular interaction network visualization suggested strong correlation between ceruloplasmin and redox metabolism, immune-related pathways, and cancer progression. We observed Ceruloplasmin expression to be correlated with negative regulators of T-cell immune response as well as shorter survival times. Our findings suggest that ceruloplasmin associated redox metabolism axis, iron homeostasis as well as immunoregulation can be targeted to develop a potential therapeutic approach for high grade OSCC patients.



