Azabicyclononane derivative downregulates the P38 MAP-kinase pathway in colon cancer through apoptosis
Keywords:
Azabicyclononane, Apoptotic assays, anticancer activity, Tyrosine kinase, Molecular docking, Protein-ligand dockingAbstract
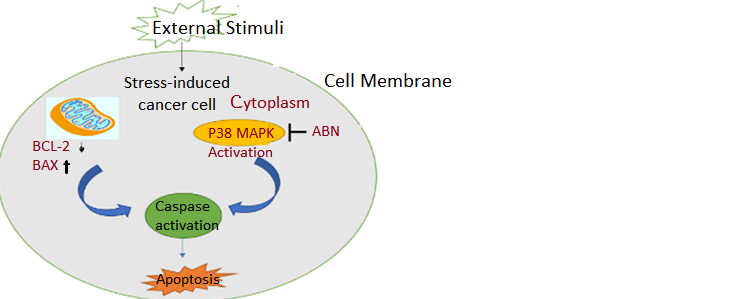
Synthesized novel azabicyclononane derivatives have been extensively analyzed for its cytotoxic, anti-cancerous activities against various cancer types. We have synthesized a set of azabicyclononane derivatives and evaluated their activity in cancer. Among the three compounds checked, ABN-5d has an IC50 value of 12.5 μM. In vitro cytotoxicity studies proved that, in addition to a significant IC50 value of ABN-5d at 25µM against cancer cell lines (HCT116), Additionally the compound also demonstrated proliferative effects in enhancing the growth of non-cancerous cells (L929). This suggested the non-toxic nature of the compound and its selectivity toward cancer cells. Apoptosis assays (Annexin V/PI, cell cycle analysis, DNA fragmentation by DPA method, DNA laddering analysis, AO/EB dual staining, and DAPI staining, Morphological analysis using SEM) confirmed that ABN-5d is inducing apoptosis in the studied cancer cells. Expression analysis of 6 genes encoding demonstrated that ABN-5d is upregulating p53 expression significantly P<0.001. Protein-ligand docking studies and western blot analysis confirmed that ABN-5d inhibits P38α MAP-kinase (binding energy -9.29Kcal/mol) and eventually downregulates the pathway. This study confirms ABN-5d as an effective anticancer agent which targets the MAPK pathway.
URN:NBN:sciencein.cbl.2022.v9.369



