Recent advances in Targeted Radionuclide therapy for Cancer treatment
Keywords:
Radionuclide therapy, targeted radionuclide therapy, radionuclides, oncology, cancer treatment, radiopharmaceuticals, PET, Radiodiagnosis, RadiotherapyAbstract
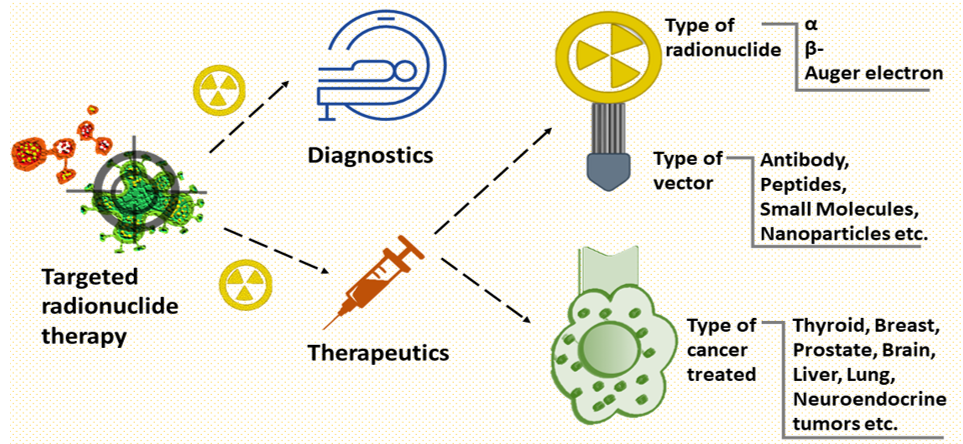
In the last two decades, science has largely evolved in methodologies for cancer treatment, yet, the basic backbone of cancer treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In oncology, radiation therapy was first used nearly a century ago but its basic principle is still in application, for example, radionuclide therapy (RNT) or targeted radionuclide therapy (TRT). TRT is effective in micro and macro metastasis and has an advantage due to low dose, high efficacy, easy targeting and treatment. The aim of this article is to overview the radionuclides, components of a TRT agent i.e., different types of radionuclides, vectors and chelators and then descriptively highlight the therapeutic potential of TRT agents in the treatment of various types of cancers, namely, breast cancer, metastatic bone pain, thyroid cancer, neuroendocrine neoplasm, prostate tumors, malignant lymphoma, brain tumors, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
URN:NBN:sciencein.cbl.2023.v10.544



