In-silico interactions of active Phytochemicals with c-MYC EGFR and ERBB2 oncoproteins
Abstract
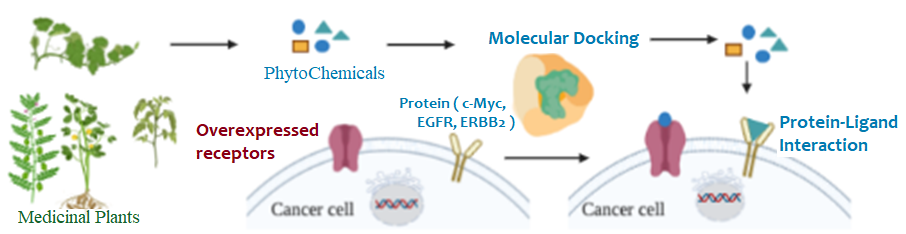
Cancer is the leading cause of mortality worldwide. Conventional chemotherapeutic agents pose a drawback as they are nonspecific. There is an urgent need to identify and design novel targets specific to the tumor. Almost 90,000 species of plants are used as a source of medicines to treat the majority of the disease including cancer. The objective of this study was to understand the interactions between the active phytochemicals selected on the basis of literature review and target oncoproteins in order to find out the biomolecules having strongest bonding actions. Molecular Docking of c-MYC, EGFR and ERBB2 with the selected Phytochemicals showed highest binding energy -7.8 Kcal/mol of EGCG with c-MYC, -8.7 Kcal/mol of Curcumin with EGFR, and -9.4 Kcal/mol of Quercetin with ERBB2. Moreover, molecular dynamics simulation data showed all three phytochemicals exhibits strong stability on their respective targets. Our studies reveal that these three phytochemicals could be promising candidates in designing and optimizing therapeutic strategies against cancer.



