In silico identification of potent FDA approved drugs against Coronavirus COVID-19 main protease: A drug repurposing approach
Abstract
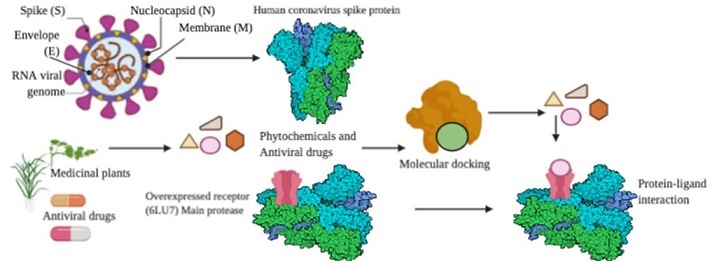
The recent outbreak of novel coronavirus disease, COVID-19 has created a threat to human population across the world. The unavailability of specific therapeutics and vaccines, demands the sincere efforts in this direction. Main Proteases of this novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) play critical role during the disease propagation, and hence represents a crucial target for the drug discovery. Herein, we have applied a bioinformatics approach for drug repurposing to identify the possible potent inhibitors of (SARS-CoV2 Main Proteases. A library of FDA approved antiviral compounds, and active phytochemicals were screened using PyRx virtual screening tool that led to 19 hits based on their highest binding affinity. Nelfinavir exhibited highest binding affinity -8.4 Kcal/mol and strong, stable interactions with the amino acid residues present on the active site of COVID-19 Main Protease. Besides, drugs including Rhein (-8.1), Withanolide D (-7.8), Withaferin A (-7.7), Enoxacin (-7.4), and Aloe-emodin (-7.4) also showed good binding affinity with favorable ADME properties. Our findings suggest that these small molecules can be used as potential inhibitors against COVID-19 Main Protease. However, further investigation and validation of these inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 are needed to claim their candidacy for clinical trials.



