In silico analysis of the role of hsa-miR-155-5p in cervical cancer
Keywords:
Cervical cancer, Meta-analysis, Gene ontology, Pathway enrichment, TCGA dataset, molecular simulations, molecular modelingAbstract
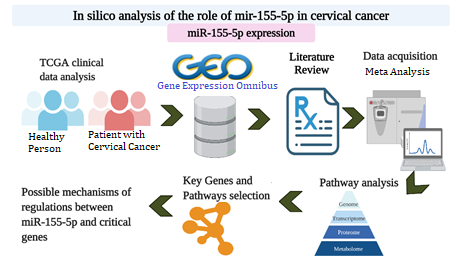
Numerous studies have established a critical role of micro-RNAs in the transcriptional regulation of multiple genes during cancer pathogenesis. Several micro-RNAs are associated with the poor prognosis and outcome of cervical cancer implicating their potential role in therapeutic intervention. The aim of this study was to determine the role of miR-155-5p in cervical cancer by performing a meta-analysis on its expression and identifying its molecular targets and pathways based on Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) dataset, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset, and literature review. Meta-analysis confirmed the upregulation of miR-155-5p expression in cervical cancer that significantly correlated with the numbers of tumour purity and histopathological grades. By using integrated bioinformatics approach, this study demonstrates that miR-155-5p could promote cervical cancer progression through targeting the expression of Sp1, EGFR, UBR4 and PIk3R1 genes. Importantly, these four genes play a crucial role in estrogen signaling pathway and choline metabolism. This study may provide future insights in revealing the mechanisms underlying pathogenesis of cervical cancer.



