Reversal of promoter hypermethylation of CADM1 and SOCS1 by leaf extract of Datura metel in cervical cancer cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.cbl.2024.v11.654Keywords:
Cervical cancer, Epigenetics, Reversal of Promoter hypermethylation, Tumor suppressor genes, Datura metel, CADM1, SOCS1Abstract
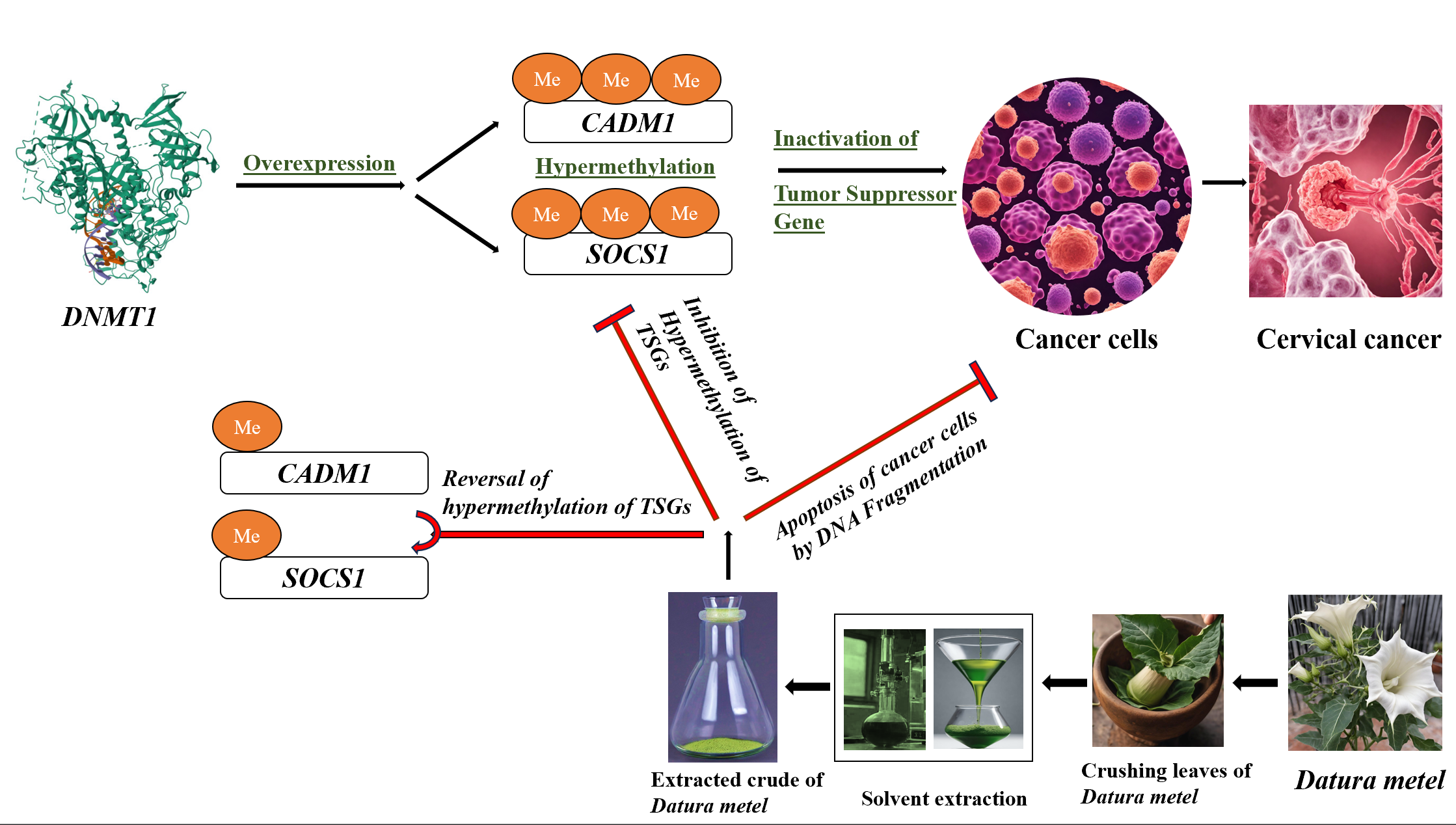
Cervical cancer ranks as the second most fatal cancer among women in developing countries, trailing only behind breast cancer. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection, among various contributors, stands as a primary cause of cervical cancer. Overexpression of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) leads to hypermethylation of Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (CADM1) and Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 (SOCS1), consequently silencing these tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) epigenetically. In this study, we explored the reversal of aberrant methylation in the squamous cervical cancer cells, SiHa using a concentration of 5 µg/ml of Datura metel ethanol- chloroform (E: C) leaf extract. Treating the cells with the extract for 72 hours and consecutively for six days, the DNA fragmentation study for cell apoptosis was performed. The methylation-specific PCR analyzed the DNA aberrant methylation patterns of these TSGs and their subsequent reversal and fragmentation. The results suggest that the Datura metel leaf extract (E: C) was able to cause DNA fragmentation and also effectively reversed the promoter hypermethylation, leading to the reactivation of CADM1 and SOCS1. This was evidenced by the reduction in intensity and visual sharpness of the methylation-specific band and the unmethylation-specific band displayed an increase in width and enhanced luminosity in MS-PCR for both genes. This study marks one of the initial global reports showcasing the potential of E: C leaf extract from Datura metel in reversing hypermethylation and reactivating CADM1 and SOCS1 genes in cervical cancer cells. Further exploration into the phytochemicals of D. metel leaves that demethylate CADM1 and SOCS1 could unveil a promising candidate for reactivating suppressed genes in cervical cancer.
URN:NBN:sciencein.cbl.2024.v11.654







