In silico screening and molecular docking study of quinoline based compounds with Human kallikrein 7 in complex with 1,4-diazepane-7-one 1-acetamide derivative receptor target for potential antibacterials
Keywords:
Quinoline, Binding affinity, Biological activity, Antibiotic, Molecular docking, Molecular modeling, In-silico study, simulationsAbstract
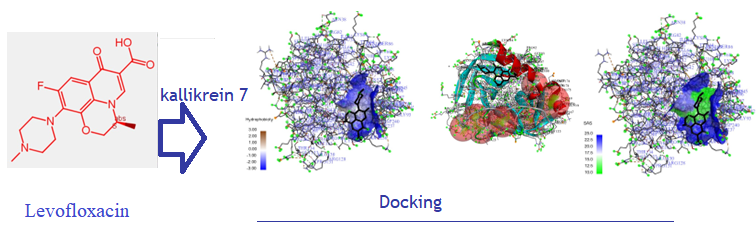
The quinolines based drugs and its analogues are widely used as a medicinal drug. In this study, five compounds from quinoline-based pharmaceuticals have been discovered using virtual screening with Autodock software, with binding affinities ranging from 6.6 to 5.4 kcal/mol. The best suitable chemical is levofloxacin, which has a higher drug-likeness and a total drug score of 0.87. Improved receptor (kallikrein 7) Vander-waal bonding with ARG A:50, TRP A:51, LYS A:243, ASN A:239, ASN A:48 is also revealed by levofloxacin docking and bonding studies. Based on the affinity score, levofloxacin was found to have superior pharmacological properties and bonding when compared to other molecules from quinoline-based drugs and kallikrein 7. After thorough in silico research, levofloxacin from quinoline-based medications can be used as a potential treatment target towards development of antibiotic medicine.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jmc.2023.585
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Shivangi Sharma, Yukti Monga, Ashu Gupta, Shivendra Singh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
