In silico screening of phenolic acids as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
Keywords:
Covid-19, SARS-COV-2, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), Molecular docking , Phenolic Acids, RNA polymerase, Heterocyclic drugsAbstract
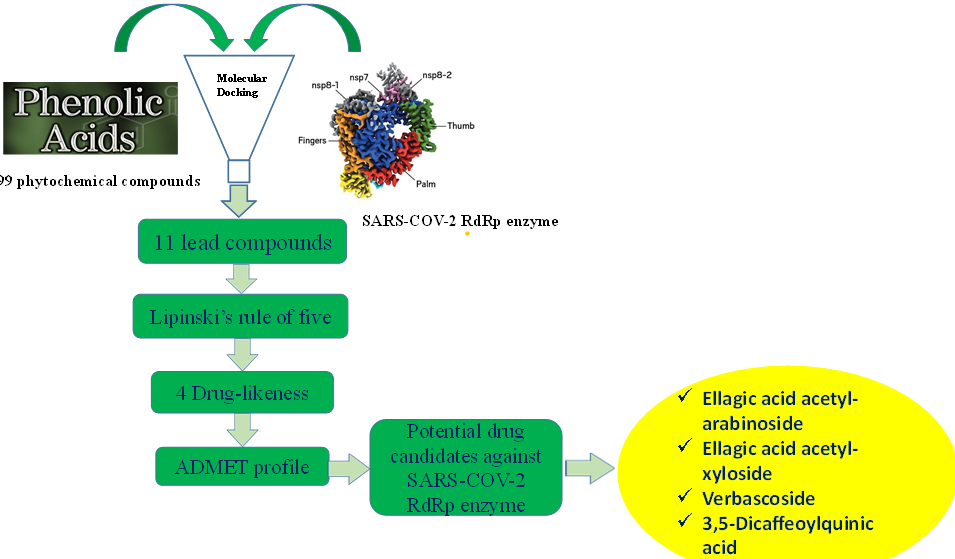
A serious public health concern is the Covid-19 pandemic that causes the acute respiratory syndrome. Thus far, Covid-19's special medicines are indeed an unparalleled obstacle for mankind. It is very essential now to find medications that can cure this disease. As a promising therapeutic target for SARS-COV-2 infection inhibition, the SARS-COV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) enzyme regulating viral replication has been evaluated. This research evaluated the potential of bioactive inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase through molecular docking in silico model. Based on the Phenol-Explorer database, we have collected 99 bioactive compounds of the phenolic acids group and compared to remdesivir, which has inhibitory activity with this protein target. 26/99 compounds that had a higher ability to inhibit the SARS-COV-2 RdRp enzyme than remdesivir were further docked targeting the active sites of SARS-CoV-2, as well as SARS-CoV and HCV RdRp. Next, 11 phytochemicals were selected through good binding energy. Predictive druglikeness and ADME/tox filtering tests were further subjected to the top docked compounds. It is suggested that four phytochemicals, namely Ellagic acid acetyl-arabinoside, Ellagic acid acetyl-xyloside, Verbascoside, and 3,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid, have good pharmacokinetic properties, which may be further explored as anti-SARS-COV-2 agents.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Bui Thanh Tung, Nguyen Bao Kim, Phan Hong Minh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
