Molecular docking study for binding affinity of Indole derivatives against solution structure of the antimicrobial peptide Btd-2[3,4]
Keywords:
Molecular docking, Indole, Amino acid, Residues, Bioactivity, Antibacterial activityAbstract
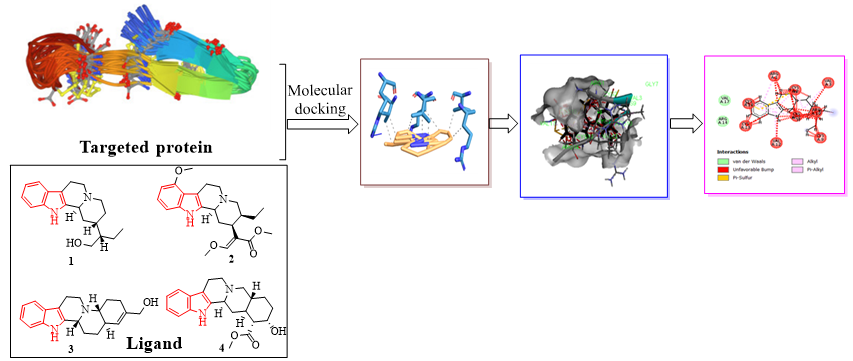
Indole based drugs are major constituents in natural products, active pharmacophores, and have excellent biological activities. The molecular docking analysis of indoloquinolizidine derivatives and solution structure of the antimicrobial peptide Btd-2[3,4] (PDB ID: 2M2Y) have been revealed in this article. The study of in silico molecular docking analysis of such indoloquinolizidine derivatives helps to determine the residual interaction, binding affinity, and hydrogen bonding of several indoloquinolizidine-based derivatives against solution structure of the antimicrobial peptide Btd-2[3,4]. The current work demonstrated that indoloquinolizidine derivatives could be very effective antibacterial agents to produce potent antibiotic medicines.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jmc.2024.686
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Shivangi Sharma

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
