Synthesis of in-silico designed plasmepsin X inhibitors and evaluation of their anti-plasmodial effects
Keywords:
molecular modeling, Plasmepsin X, Hydroxyethylamine, Piperazine, Plasmodium falciparum, Molecular docking , anti-malarial activityAbstract
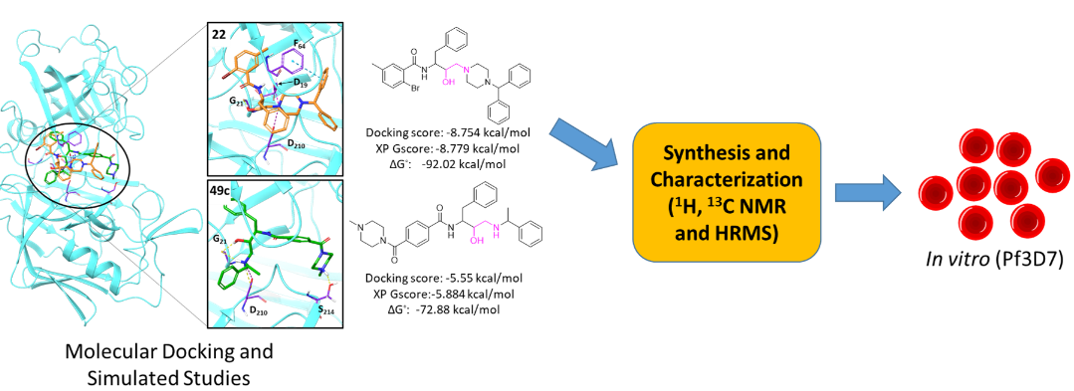
Plasmepsin X (PfPlm X) protein plays a significant role in egression and invasion of malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum (Pf) and is considered a promising target. All hydroxyethylamine (HEA) and piperazine based 313 analogs were screened against PfPlm X protein. In computational study, compound 22 was identified as the most promising molecule which showed better docking results compared to 49c. Compound 22 showed docking scores, XP Gscore, and ∆G˚ of –8.754 kcal/mol, –8.779 kcal/mol, and –92.02 kcal/mol, respectively while 49c showed docking score, XP Gscore, and ∆G˚ of -5.550 kcal/mol, -5.558 kcal/mol, and -72.88 kcal/mol, respectively. An extensive MD simulation of 200ns also supported the docking results of compound 22. Assayed for the initial screening against Pf Chloroquine (CQ)-resistant (INDO) culture suggested that compound 22 is a hit molecule with an inhibitory concentration of 6.8 µM. Next, compound 22 was also assessed for toxicity against liver cells, HepG2, and none of the two compounds showed cytotoxicity up to 100 µM. Overall, compound 22 demonstrated moderate anti-plasmodial activity without any toxic effects, and therefore medicinal chemistry optimization is essential to obtain analogs with improved inhibitory activity.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jmc.2022.443
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Smriti Sharma, Kunika Saini, Vinayak Bhatia, Sheza Zaidi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
