Molecular docking of phytochemical compounds in Cucurbita maxima with anti-prostate cancer activity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jmc.2024.685Keywords:
Prostate cancer, Phytochemicals, Molecular docking, cancer drug, Heterocyclic drugsAbstract
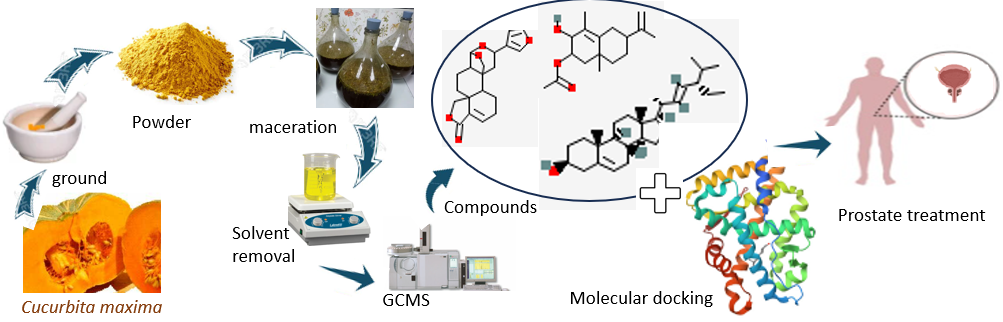
Cucurbita maxima seeds are used in traditional medicine for the treatment of urinary disorders, blood pressure regulation and prevention of constipation, also for wound healing with dermal application, and recently for prostate cancer treatment. The objective of present study was to identify the medicinal compounds present in chloroform extract of the seeds of Cucurbita maxima using Gas chromatography mass Spectroscopy (GCMS). The phytochemicals identified were further assayed to determine the compounds associated with anti-prostate activity using in silico molecular docking. The GCMS analysis revealed the presence of twenty-three (23) compounds. The molecular docking of the compounds against Human Androgen Receptor Ligand binding showed that the compounds had good binding affinity against the target protein. However, two compounds, Stigmasterol (-8.5 kcal/mol), and Bacchotricuneatin C (-7.7 kcal/mol) had better binding affinity than the control anti-prostate cancer drug, Enzalutamide (-7.6kcal/mol). Consequently, the results validate the use of the seed of cucurbita maxima as an anti-prostate cancer agent.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jmc.2024.685
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Chinyere B.C. Ikpa, Nneoma Ngozika Chidozie-Ikpa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
