Molecular docking studies of phytocompounds from Artemisia monosperma against ERK2 kinase in lung cancer
Keywords:
Lung Cancer, ERK2, Catechol, Andrographolide, β-Sitosterol, Artemisia monosperma, Antitumor, phytochemicalsAbstract
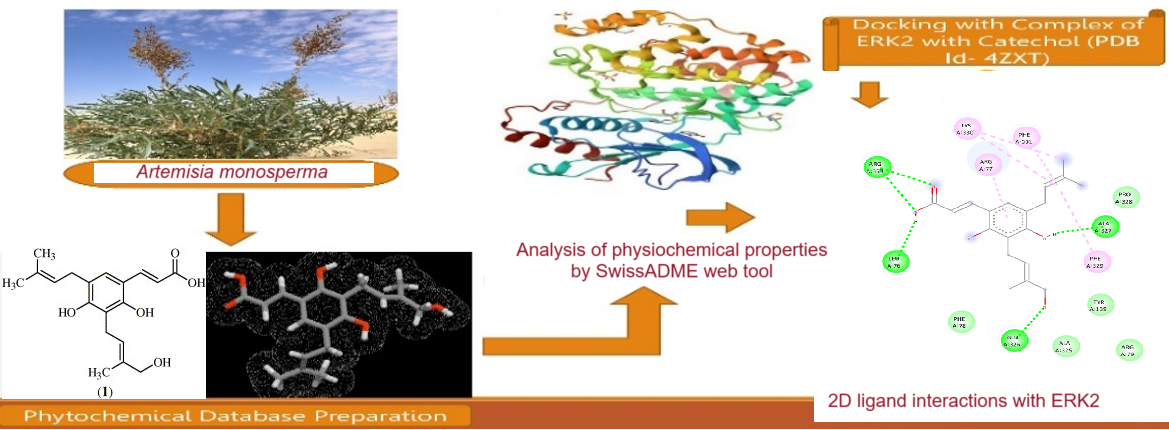
Plants contain secondary metabolites with pharmacological properties. The focus is on commercializing natural bioactive compounds. We focused on studying Artemisia monosperma for therapeutic potential against lung cancer using in-silico studies. EGFR/RAS/MAPK signaling induced by various carcinogens is critical in lung cancer development. Many lung cancer patients exhibit constitutive activation of ERK2, making compounds targeting ERK2 in lung carcinogenesis beneficial. Treatment with catechol caused lung cancer cells to be arrested in the G1 phase and reduced protein expression linked to G1-S progression. Artemisia species have various therapeutic uses in traditional medicine worldwide. They possess anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antioxidant, antispasmodic, antimicrobial, insecticidal, antimalarial and antifungal properties. Through molecular docking-based virtual screening, a compound called 4, 6-Dihydroxy-3-(3-Methyl-2-Butenyl)-5-(4-Hydroxy-3-Methyl-2-Butenyl) Cinnamic Acid was identified as the best hit with a MolDock score of −6.96 kcal/mol. This compound was found to be drug-like according to Lipinski's rule of five, and its ADMET features displayed average pharmacokinetic profiles.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jmc.2023.591
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Surya Pratap Gurjar, Arpita Roy, Aaryan Gupta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
