Molecular docking and dynamic studies of novel phytoconstituents in an investigation of the potential inhibition of protein kinase C- beta II in diabetic neuropathy
Keywords:
Diabetic neuropathy, Computational biology, PKC-beta II, Hydrangenol, Phyllodulcin, Molecular Dynamic studyAbstract
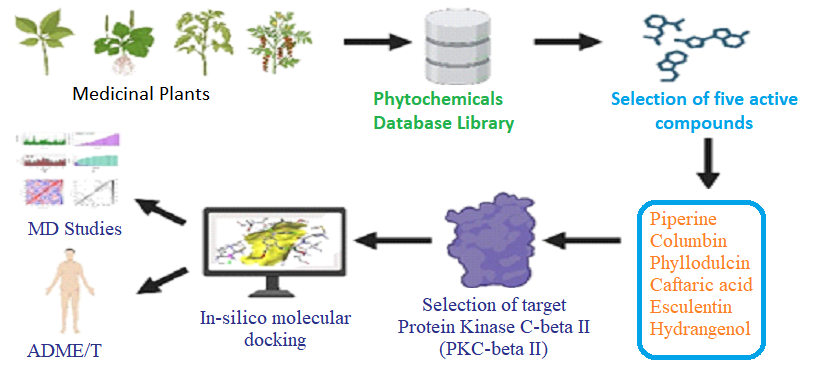
Diabetic neuropathy, a debilitating complication of diabetes, necessitates innovative therapeutic interventions targeting Protein Kinase C-beta II (PKC-beta II). This study derives its rationale from the established antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hypoglycemic attributes of Piperine, Columbin, Phyllodulcin, Caftaric acid, Esculentin, and Hydrangenol. The primary objective is to computationally unravel the inhibitory potential of these phytoconstituents against PKC-beta II. Methodologically, molecular docking employing AutoDock Vina facilitated the assessment of binding affinities. Swiss ADME and pkCSM platforms were harnessed for ADME attributes and toxicity profiles, ensuring compound safety and absorption. Molecular dynamics simulations via GROMACS ensured the stability of protein-ligand complexes. Calculations of binding free energy, hydrophobic interactions, charge distribution, aromatic character, and Surface Area Solvent (SAS) augmented the evaluation of PKC-beta II inhibitory potential. High-throughput screening, comparing with established inhibitors, further corroborated their promise. In culmination, the computational exploration demonstrates the propitious inhibition potential of the selected phytoconstituents against PKC-beta II, substantiated by favorable binding affinities, robust ADME profiles, and molecular dynamics stability.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jmc.2023.589
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Vishesh Kumar Maurya, Sanjesh Kumar, Mansi Singh, Vikas Saxena

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
