Expatiating the pivotal role of Dendrimers as emerging nanocarrier for management of Liver Disorders
Keywords:
Liver Disorders, Dendrimers, Drug Delivery, Divergent Approach, Convergent Approach, Orthogonal CouplingAbstract
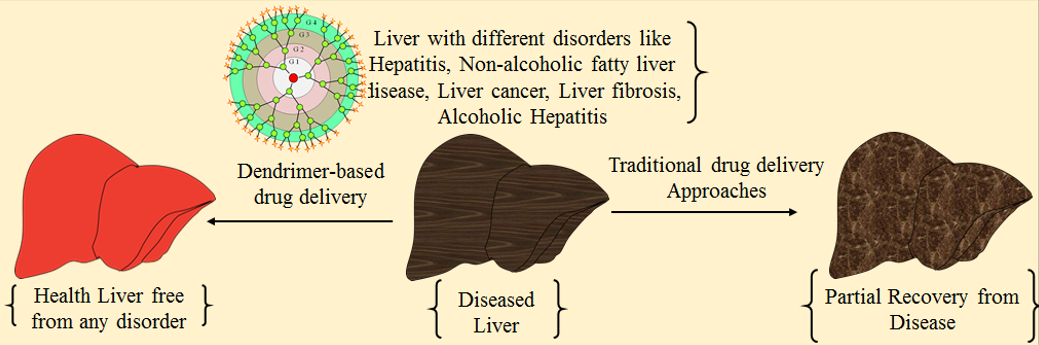
Despite advancements in medical science, liver disorders remain to be significant global health challenge, and drug toxicity frequently makes pharmacological therapy difficult. Dendrimers are polymeric three-dimensional structures with a central core, branches, and functional groups at their ends which have distinguished characteristics like high aqueous solubility, well-defined structure, biocompatibility and high encapsulating efficiency for numerous drugs. These have high ratio of terminal groups to molecule volume and therefore acts as potential drug delivery vehicle. Dendrimers have considerable potential to improve biological and physicochemical properties of drugs like enhanced solubility, bioavailability and drug targeting via transporting drugs to their targets at lower dosages, considerable potential for increasing drug safety and minimizing drug-related toxicity. In recent decades, significant improvement has been achieved in utilization of dendrimers in therapeutic, preventive and diagnostic purposes for management of liver diseases. This review highlights about structure and chemistry of dendrimers, dendrimer synthetic approaches i.e. divergent approach, convergent approach, orthogonal coupling and double exponential approach, brief summary of different liver disorders, drugs used for treatment of liver disorders, advantages of dendrimer based drug delivery over conventional systems and applications of dendrimers as nanocarriers for therapeutics of liver disorders. Patent literature status related to application of dendrimers in liver disorders has been updated in this review.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2023.v11.489
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Neelam Sharma, Ishrat Zahoor, Sukhbir Singh, Tapan Behl, Anita Antil, Hema

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



