Development and optimization of Hydrotropic Solid Dispersion of Dexlansoprazole using Central Composite Design approach
Keywords:
Dexlansoprazole, Crystalline, Hydrotropic Solid Dispersion, Solvent Evaporation Technique, Sodium Acetate, Sodium AlginateAbstract
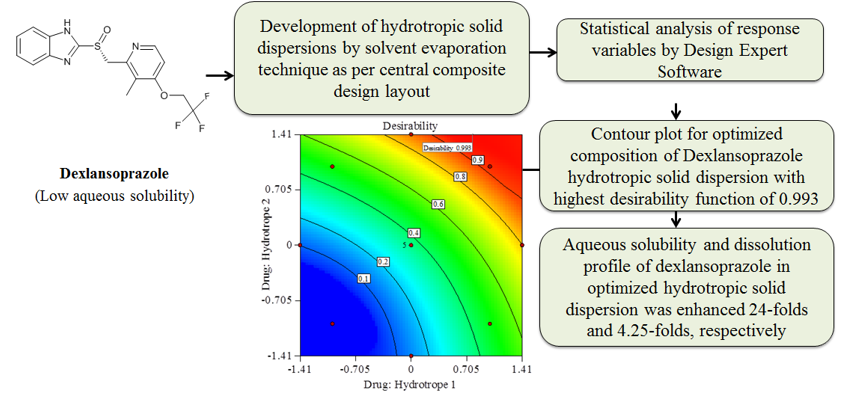
The objective of current research aims to enhance dissolution of dexlansoprazole (DLP) by organic solvent free and environment friendly approach through synthesis of hydrotropic solid dispersion (HSD) using water by solvent evaporation technique using sodium acetate and sodium alginate as hydrotropic agents. Central composite design was applied to analyze effect of drug: sodium alginate (X1) and drug: sodium acetate (X2) on response variables i.e. Q15 (Y1), Q45 (Y2), Q90 (Y3), t10% (Y4) and t50% (Y5) using Design Expert Software. This was revealed that quadratic model was superlative on account of insignificant p-value (p>0.05) for lack-of-fit analysis. The favourable values of optimized DLP-HSD were drug: sodium alginate (1: 2.78) and drug: sodium acetate (1: 4.41) which demonstrated highest desirability function (0.993). The study demonstrated that aqueous solubility and dissolution profile of DLP in DLP-HSD was enhanced 24-folds and 4.25-folds, respectively. This research conclusively manifested that hydrotropic solid dispersion hold enormous potential as organic solvent free and therefore, environmental friendly technique for enhancing solubility and dissolution of BCS class II drugs.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2023.v11.559
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ritu Gulia, Sukhbir Singh, Sandeep Arora, Neelam Sharma

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



