Competitive inhibition of catechol from Andrographis paniculata in the complex of ERK2 in lung metastasis
Keywords:
Andrographis paniculata, Lung Cancer, ERK2, Catechol, β-Sitosterol, Molecular ModelingAbstract
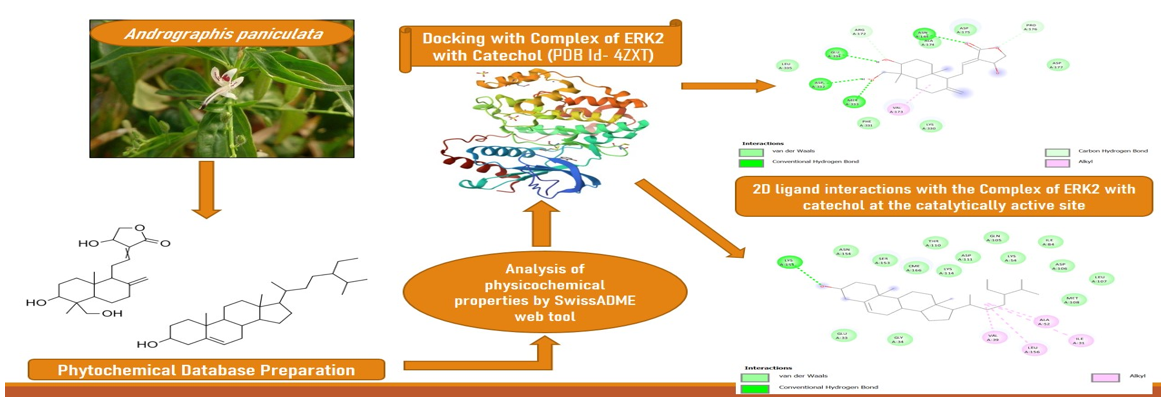
Lung cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide, affecting 18% of cancer patients. There are already 15 drugs available on the market, but their side effects are severe, causing serious damage to other tissue systems, such as white blood cells. To combat these severe problems, alternative therapies are required. Use of medicinal plants is one such option. Andrographis paniculata is a medicinal plant used for treating diseases such as cancer, diabetes, high blood pressure, ulcers, leprosy, bronchitis, skin conditions, influenza, dysentery, dyspepsia, and malaria. This study aims to evaluate the role of bioactive compounds of Andrographis paniculata against a target ERK2 (Extracellular Signal-related kinase). Two compounds are identified that show more than - 8.00 kcal/mol binding energy, and they are Andrographolide and β-Sitosterol. The molecular analysis and ligand orientation were studied with the help of the computational approach. The binding and intermolecular energy show that the compounds can be explored further in vivo to develop drugs against lung metastasis. Andrographis paniculata has the potential to cure lung metastasis by alleviating drug side effects and severe damage to other tissue systems.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.719
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Surya Pratap Gupta, Arpita Roy, Aaryan Gupta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



