Development of Benzimidazole a promising scaffold against Breast cancer via in silico approaches
Keywords:
Breast cancer, Molecular Modeling, Computer simulations, Docking, Molecular Targets, heterocyclic compounds, clinical drugsAbstract
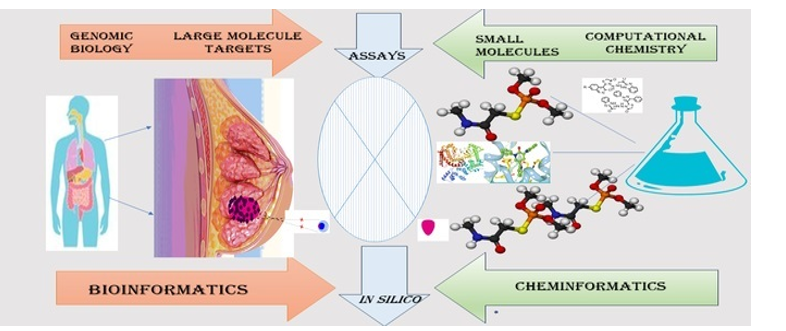
Computational techniques offer useful tools for lead identification, optimization, and target selection in the search for many therapeutic candidates for breast cancer. It is well known that benzimidazole and its derivatives are important players in the development of novel anticancer drugs. Computational methods help to streamline the drug discovery process, reduce costs, and increase the chances of identifying effective treatments for this complex disease. As is commonly accepted, discovering new drugs is a difficult, slow, and affluent process. According to estimates, the typical drug development pipeline takes 12 years and costs $2.7 billion to produce a new drug. The pharmaceutical sector is struggling to find a solution to the difficult and pressing issue of how to minimize research costs while expediting the development of new therapies. The development of computer-aided drug discovery (CADD), is a potent and optimistic technique for developing medications rapidly, inexpensively, and efficiently. Recent advances in computational drug discovery technologies have substantially influenced the development of drugs to treat Breast Cancer. To identify leads, computational methods offer useful tools. In the present study, a computational study on benzimidazoles and their derivatives against Breast Cancer targets have been provided.
URN: NBN: sciencein.jist.2024.v12.714
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 jyoti Monga, Niladry Sekhar Ghosh, Minky Mukhija, Sonia Kamboj, Ranjit Singh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



