In-silico molecular studies of the phytochemicals in ethanolic extract of Chromolaena Odorata against H+/K+-ATPase enzyme for Proton Pump inhibitor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2024.v12.801Keywords:
Omeprazole, gastric pump, ulcer, In-silico study, Phytochemical Constituents, Molecular Modeling, ChemistryAbstract
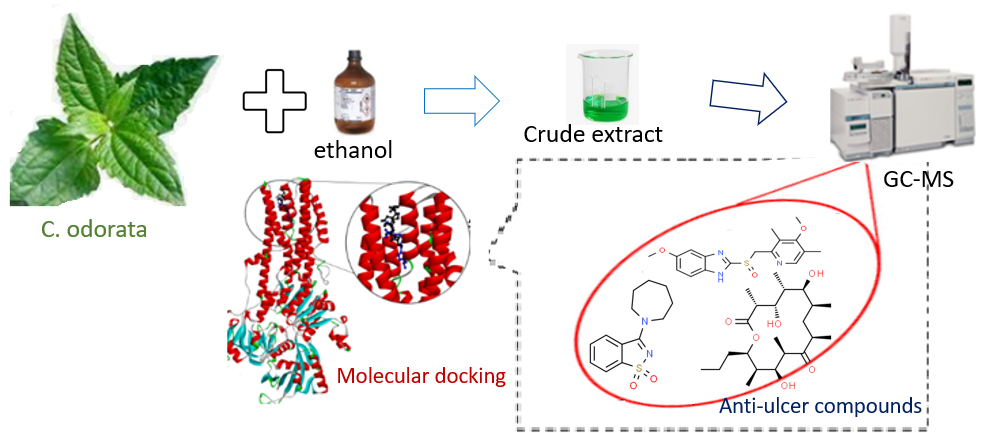
Chromolaenaodorata popularly called devil weed (independent leaves) is a subtropical flowering shrub in the family of Asteraceae that has been used for the herbal treatment of wounds, burns, skin infections, and relieving painful stomach ulcers. There are some scientific literature reporting its antimicrobial, wound healing, hemostatic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, platelet protective, anticancer, hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic, insecticidal, and anti-anemic properties. This study investigated the phytochemical components and the anti-ulcer (gastric pump inhibition) properties of the ethanolic extract of the plant using GC-MS and in silico molecular docking. The GC-MS results from this study detected thirty (30) retentions with fifty-one (51) library/ID-suggested compounds. The docking of the detected compounds against gastric proton pump for the treatment of ulcer revealed that among the ligands that were docked with the enzyme (H+/K+-ATPase); (3-(Azepan-1-yl)-1,2-benzothiazole 1,1-dioxide) had better binding energy value (high binding energy value) (-8.4kcal/mol) compared to the standard anti-ulcer drug (omeprazole; −8.0 kcal/mol). The strong bonding of 3-(Azepan-1-yl)-1,2-benzothiazole-1,1-dioxide to the receptor suggests that the compound may possess better gastric proton pump inhibitory potential than omeprazole. This result may also validate the traditional use of the plant for gastric ulcer-relieving activity.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.801
Downloads
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Chinyere B.C. Ikpa, Oluwatosin Maduka Tochukwu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission







