2-Styrylquinoline and its derivatives: Study of medicinal, electronic and spectral properties using density functional theory
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2025.v13.1173Keywords:
2-Styryl quinoline, Density functional theory (DFT), Energy gap, Nonlinear Optical Characteristics, heterocyclic compounds, Semiconductor, metal complexAbstract
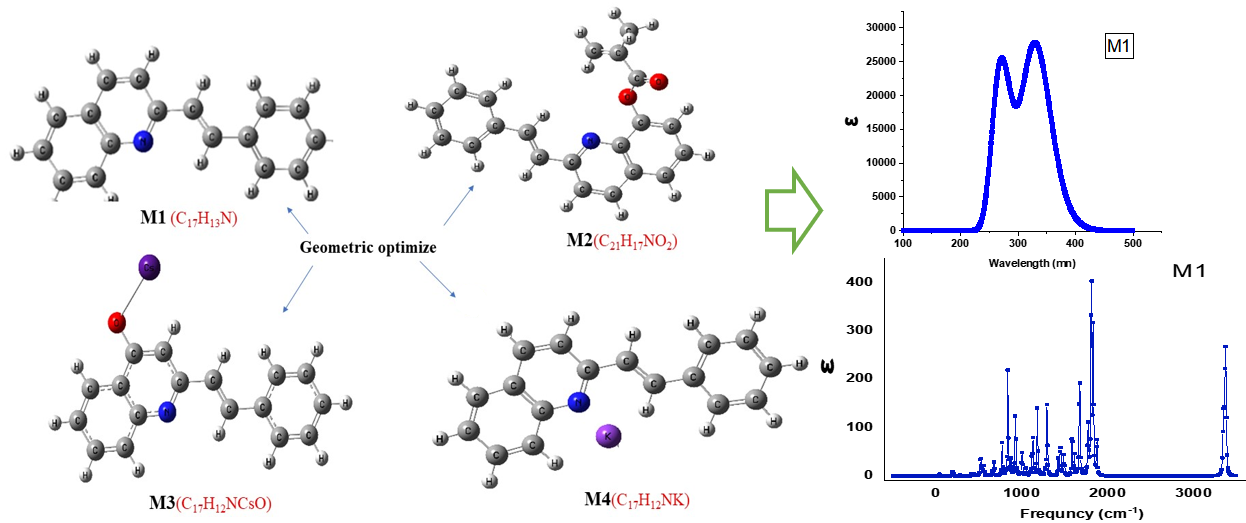
2-Styryl quinoline ((M1) C17H13N) is biologically active compound that has various medical, optical and electronic applications. A density functional theory (DFT), and the B3LYP/6-311+G basis set were used to study the electronic, vibrational, and nonlinear optical properties of 2-styryl quinoline and it derivatives, ((M2) C21H17NO2, (M3)C17H12NCs+O, (M4)C17H12NK).The optimized structure, Egap, and IR, NMR, and UV spectra of the molecular electrostatic potential (MEP) were calculated to provide a brief understanding of the behavior of these compounds. The results showed a slight decrease of energy difference between HOMO and LUMO from 3.8 eV for M1 to 3.7 eV for M2. In contrast, the energy gap for M3 and M4 was initially measured at 7.1 eV (M3) and 2.2 eV (M4), eventually reaching 2.25 eV. These results demonstrate the good semiconducting character of the obtained compounds. Among the studied compounds, M4 has the highest dipole moment (11.925 D) and the highest polarizability value (-91.032 D) compared to the other compounds. Hence, the doping with cesium is possible because the large size of the cation enhances its interaction with the oxygen atom. The addition of a cesium atom to the monomer is a good step to enhance the medicinal properties. Therefore, the doping process is a suitable method to enhance the optoelectronic properties of pristine 2-styryl quinoline.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Huda M. Jawad, Abbas Shwya Alwan, Anees Abdulmunim Mohammed

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission







