Enhanced optical, electrical, dielectric, and photovoltaic properties in strontium titanate by Ce-doping through a modified combustion method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2024.v12.781Keywords:
Perovskites, dye sensetized solar cellAbstract
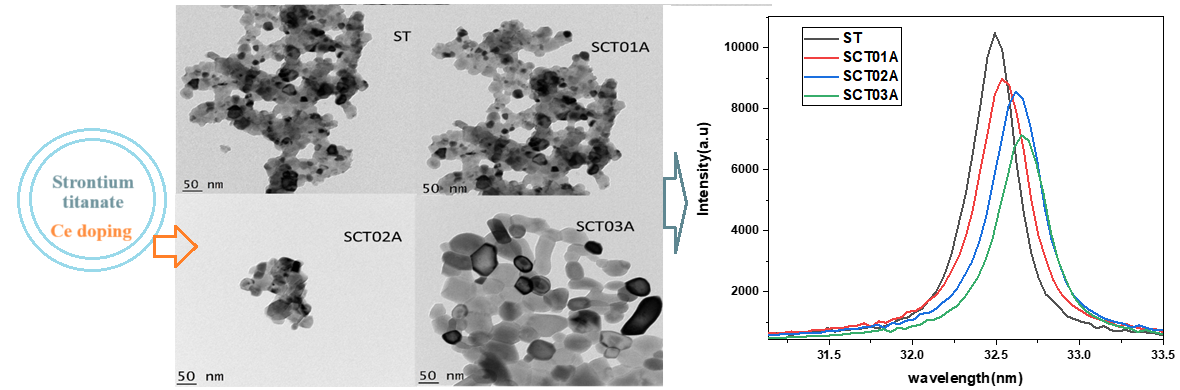
Structural, optical, electrical, dielectric, and photovoltaic characteristics of compounds with the chemical formula Sr(1-x)CexTiO3(x=0,0.01,0.02,0.03) is examined in this article. A set of single-phase compounds were created using a modified combustion process. X-ray diffraction examination at room temperature verified cubic phase with P3mm space group The dimension of the crystallites obviously increased after doping with cerium, according to HRTEM images. The FTIR spectra showed an indication of metal-oxide vibration-related peaks. Due to the introduction of midgap states with doping, the bandgap decreased with cerium infusion from x=0 to 0.03 as shown by UV-visible spectroscopy, raising the prospect of photovoltaic applications. Upon the dielectric characterization, each compound's dielectric constants and losses had an identical behavioural pattern: both were higher in the low-frequency region and rapidly decreased as frequency ascended until stabilizing. The dielectric constant in strontium titanate went up with A-site cerium doping in the perovskite strontium titanate. The loss factor increased for the cerium-doped sample in the low-frequency range and decreased in the mid-frequency region. The conductivity and frequency response of all materials followed Jonscher's power law. The total electrical conductivity increased in the doped samples. The electrical conductivity of the doped samples was improved by the reduction in activation energy brought on by doping. The electrical conductivity increased with an increase in temperature for all of the dense ceramics. The DSSC performs more effectively when utilizing a cerium-doped sample as the photoanode than when using an undoped sample.
URN: NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.781
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Rini Varghese, Steffy Maria Jose, J.S. Lakshmi, A Abraham, Jijimon K Thomas

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission







