The in vitro and in silico assessment of the proliferative and angiogenic potential of Substance K: Interaction of Substance K between the Neurokinin-1, Neurokinin-2, and Tie-2 receptor proteins
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.cbl.2024.v11.672Keywords:
Substance K, Neurokinin-A, Angiogenesis, Substance P, NK-1, NK-2, Tie-2, VEGFR, cell proliferationAbstract
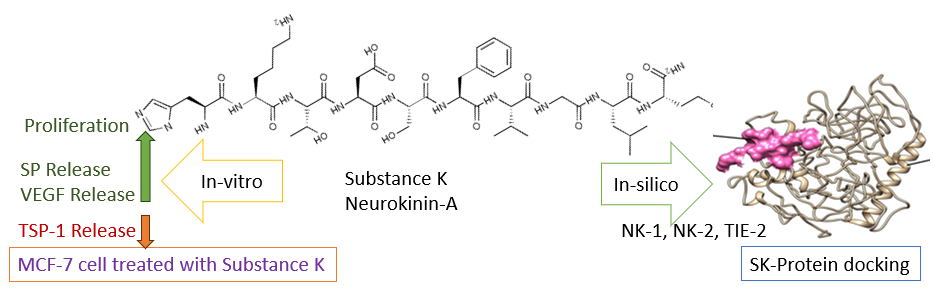
Substance K is a neurotransmitter peptide, with neurological activity. SK shows similar effects with Substance P on cell proliferation. This study aims to determine whether SK has the potential to act on cell proliferation and angiogenesis via in vitro and in silico methods. MCF-7 cells were treated with different doses of SK and the cytotoxic effects on the proliferation of cells were determined via a WST-1 kit. VEGF, SP, and Thrombospondin-1 levels in media were evaluated via ELISA kits. In silico assessment was done to determine the possible interaction of SK with NK-1, NK-2, NK3, Scara5/SRCR domain, VEGFR-1, VEGFR2, CD36, NRP1, Tie-2, and PDGFR receptor proteins. Molecular docking studies were performed via HPEPDOCK 2.0, MDockPeP, and CABS-dock. Substance K exhibits both proliferative and angiogenic properties on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, as predicted. According to our molecular docking results, SK effectively binds NK-1, NK-2, and Tie-2 receptors and probably this could be one of the possible reasons for its angiogenic properties. This is the first report showing that the SK could mimic SP and act as an angiogenic factor based on its interactions with NK-1, NK-2, and Tie2 important angiogenic receptor proteins.







