Effects of 1,3-di-O-substituted-myo-inositol derivatives on the antiproliferation and caspase-3 activity of HCT-116 and HL-60 cells
Abstract
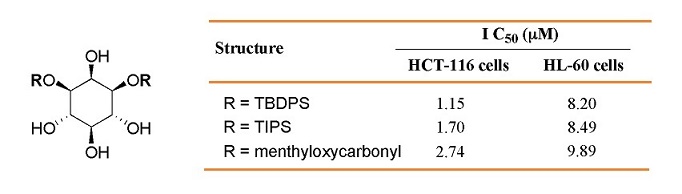
The functionalized myo-inositols, 1,4,5-triphosphoinositol and posphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-triphosphate, are intracellular signaling molecules. Using a one-step regioselective functionalizing method, we synthesized 1-mono-O- and 1,3-di-O-substituted-myo-inositols and then evaluated their in vitro antiproliferative effects on two human tumor cell lines, HCT-116 colon tumor cells and HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cells. The 1,3-di-O-substituted-myo-inositol, containing menthyloxycarbonyl, tert-butyldiphenylsilyl ether (TBDPS), and triisopropylsilyl ether (TIPS), potently inhibited the growth of both types of tumor cells, and exhibited IC50 values of 2.74, 1.15, and 1.70 mM for HCT-116 cells and 9.89, 8.20, and 8.49 mM for HL-60 cells, respectively. The cytotoxic effects of the three disubstituted-myo-inositols on HL-60 cells were dose- and time-dependent, and these molecules also activated caspase-3, which is used as an index of cell apoptosis, within the cells. These findings indicate that 1,3-disubstituted, but not 1-monosubstituted, myo-inositols activated caspase-3 and prevented the proliferation of HCT-116 and HL-60 tumor cells.



