Electrochemical and morphological investigation on Corrosion Inhibition of Mild steel in 1N HCl by leaf extract of Pongamia pinnata
Keywords:
AC Impedance Spectroscopy, Atomic Force Microscopy, FTIR, Green Inhibitor, Potentiodynamic polarization, Corrosion, Corrosion inhibitor, Steel Corrosion, Corrosion in AcidAbstract
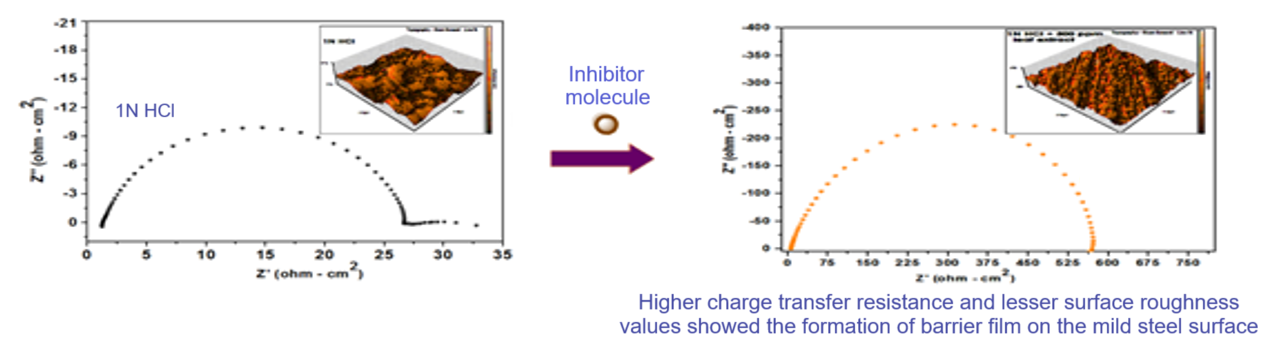
The corrosion inhibition potential of Pongamia pinnata (P.pinnata) was investigated for mild steel corrosion in 1N HCl using electrochemical methods viz., Potentiodynamic Polarization and AC Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS). Spectroscopic techniques such as UV-Vis, FT-IR, GCMS, SEM and AFM techniques were used for characterization and morphology studies. From the results of potentiodynamic polarization, it is found that inhibition efficiency (I.E %) increases while increasing the concentration of leaf extract molecules, the highest inhibition efficiency of 95.5% is observed at 300ppm leaf extract. Tafel curves showed mixed type behaviour of inhibitor and results obtained from EIS studies confirmed the single charge transfer reaction of corrosion process. The inhibitor molecules obey Langmuir adsorption isotherm. FTIR, SEM and AFM results also supported the effectiveness of P.pinnata as good corrosion inhibitor for mild steel corrosion in acid medium. The results obtained from electrochemical methods are fairly agreed with the results arrived from spectral results.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jmc.2022.468
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2022 C. Jeyaprabha, T.K. Bhuvaneswari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
