Effect of heat on phytochemical profile and antioxidant activity in Amla (Emblica offinalis) fruit extract
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2025.v13.1146Keywords:
Amla extract, Hydrolysable tannoids, gallic acid, Ascorbic acid, ellagic acid, Antioxidant activity, Phytochemical screeningAbstract
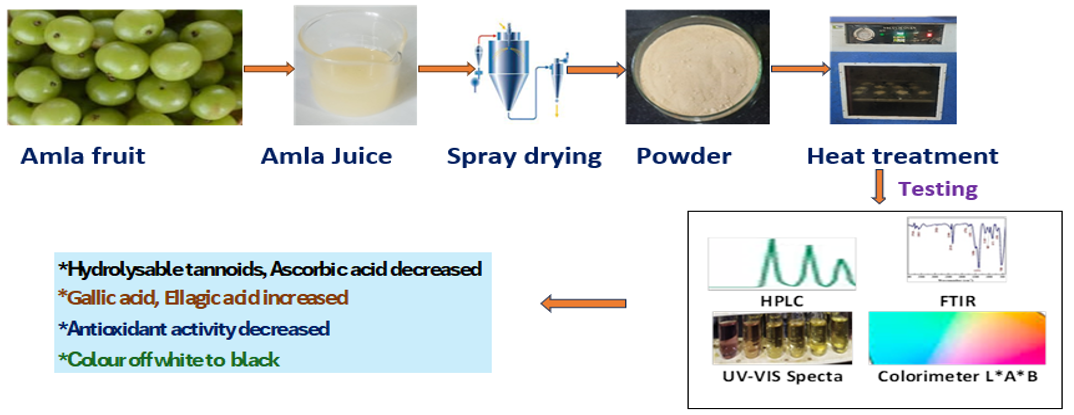
In this study the effect of heat (80°C to 120°C) on phytochemical profile and antioxidant activity in fresh Amla (Embolic officinale) juice powder has been investigated. The fresh amla juice powder was prepared by spray drying technique and further additional heat treatment was given in hot air oven. The hydrolysable tannoids content reduced from 21.86±0.45% to 0.75±0.2% at 120°C after treatment for 36 hours. Gallic acid increased from 0.85±0.05% to 11.80±0.16% and ellagic acid increased from 0.78 to 2.33%. The Ascorbic acid content is reduced from 4.68±0.07% to 0.17±0.02%. The increase in gallic acid content was also supported by FTIR analysis. The purity Index against gallic acid increased from 0.8429 (untreated Amla powder) to 0.8821 (amla powder treated at 120°C for 36 hours). The LAB value was changed from 87.27 *0.52 * 18.4 to 42.24 *1.49*(-)1.35. The antioxidant activity decreased remarkably at 120°C. Thus, the alteration of chemical composition takes place because of dehydration and other chemicals reaction affected by Heat.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ajay Kumar Pathak, Vedant Rakesh Gupta, Rambir Singh, Arvind Kumar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission







