Normalized difference vegetation index and land surface temperature evaluation of agricultural land near Ujani Dam Solapur district using TIMESAT software
Keywords:
TIMESAT, Land Surface Emissivity (LSE) , Brightness Temperature , Planck’s function, Radiative Transfer Equation (RTE) , Vegetation prediction, Normalized difference vegetation index NDVI, satellite imagesAbstract
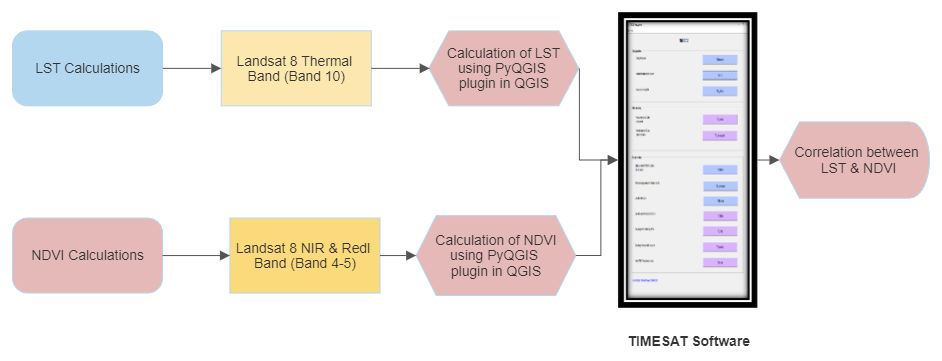
The fusion of normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and land surface temperature (LST) provides very important information for analyzing systems such as agricultural drought monitoring system or drought early warning system. This research paper focuses on the study of the relation amongst land surface temperature and normalized difference vegetation indices using time series composed of Landsat 8 satellite OLI/TIRS sensor data. For deriving LST, the Radiative Transfer Equation (RTE) algorithm and the Planck’s function have been used with a PyQGIS plugin of Landsat 8 TIRS data. Along with LST and (NDVI), at-sensor reflectance, Land Surface Emissivity (LSE) and brightness temperature are also calculated using the PyQGIS plugin. TIMESAT software is used for estimation of phenological parameters which helps in understanding the growth of crops at different stages, effects of climate changes on crops and finding the relation between LST and NDVI. It has been observed that LST and NDVI are strongly negatively correlated. Planck’s function gives the best negative correlation result as compared to the RTE algorithm. Also, various adjustment methods such as Savitzky Golay and Double Logistic Function are used for computation of seasonality parameters and it can be observed that Double logistic gives the best results.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.735
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Manisha Kumawat, Arti Khaparde, Mehul Pandya, Pooja Pawar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



