Adipokines as immune modulators in inflammation mediated male infertility
Keywords:
Adipokines, adipose tissue, inflammation, immune-modulation, male infertilityAbstract
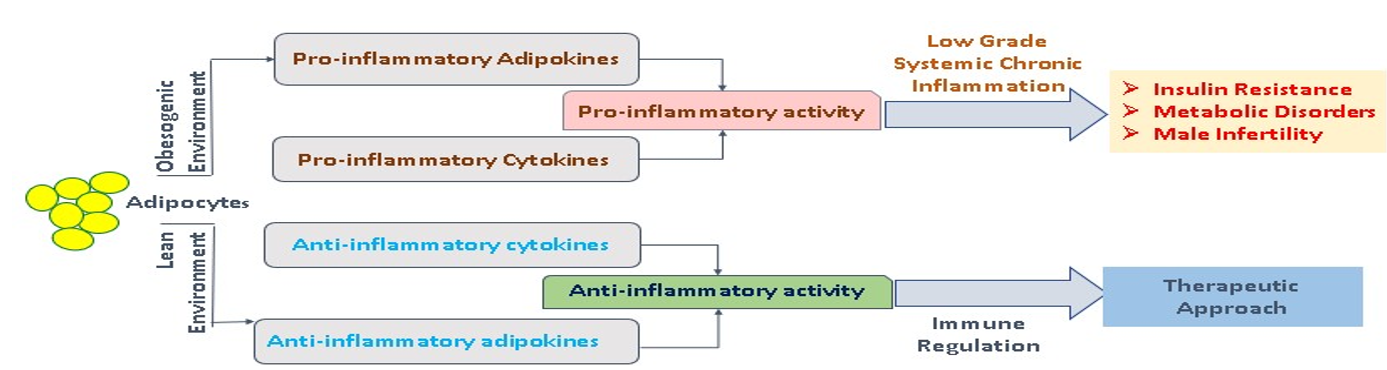
Adipose tissue has widely been explored for it functions in energy storage and release, thermal insulation, non-shivering thermogenesis and even for endocrine functions. In addition, adipose tissue contains numerous immune cells such as B cells, T cells, macrophages, and neutrophils, and obesity affects both the number and properties of the immune cell subtypes, revealing adipose tissue as an active immunological organ that can influence the metabolism as a whole via paracrine and endocrine mechanisms. During obesity the combined action of proinflammatory adipokines and cytokines may give rise to inflammation which may further lead to insulin resistance and may develop a variety of metabolic disorders and in some cases even inflammation mediated male infertility. Adipose tissue is said to have a unique group of immune cell that mediate both innate and adaptive immunological responses. A more extensive study must be performed to comprehend the molecular mechanisms linking obesity to infertility. This review aims to accentuate the understanding of how adipokines may act as immune-modulators, which might lead to unveiling of therapeutically relevant mechanisms that govern adipose tissue inflammation, and thereby various metabolic diseases.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2023.v11.573
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Silpi Acharyya, Sulagna Dutta, Pallav Sengupta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



