Investigating the doping effects on the optical, electrical, structural, morphological, elemental composition, and magnetic properties of electrodeposited Ti-doped CuS thin films
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.mns.2025.V12.1191Keywords:
DMS;, electrodeposition;, Ti doping; , bandgap;, UV-VIS spectroscopy; , XRD; , SEM-EDS;, four-point probe; , VSMAbstract
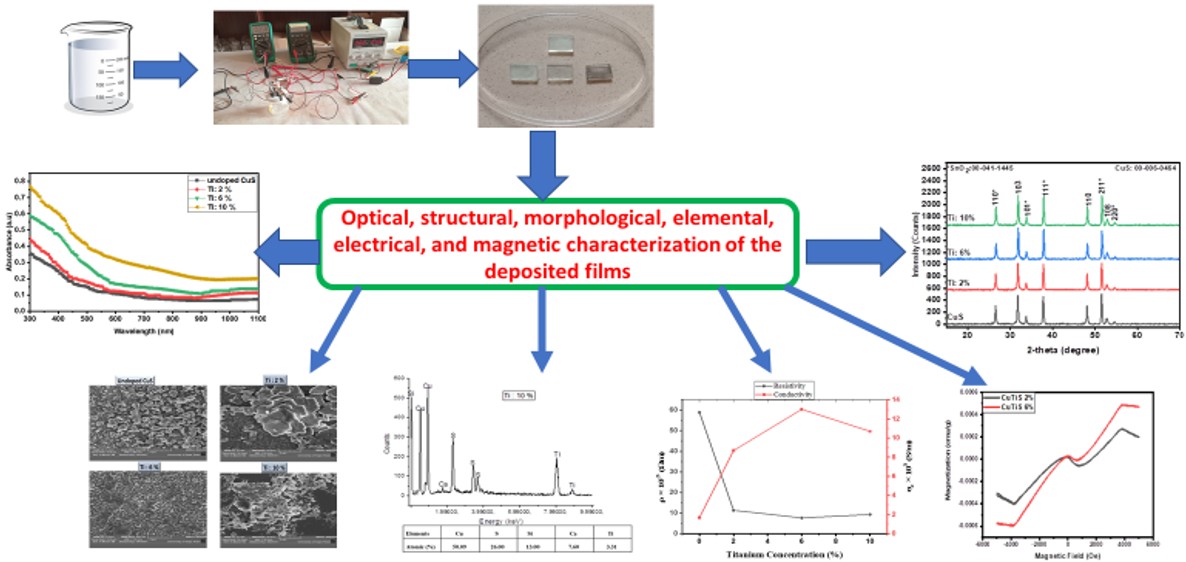
Thin films of copper(II) sulfide (CuS) and titanium-doped copper(II) sulfide (Ti:CuS) were successfully deposited on fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass substrates using the electrodeposition technique at room temperature. The films were characterized to evaluate their optical, structural, morphological, compositional, electrical, and magnetic properties. The characterization techniques included UV-Vis spectrophotometry (in the wavelength range of 300–1100 nm), X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), four-point probe method, and vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM). Film thicknesses were measured using a profilometer, yielding values of 109.16 nm for undoped CuS, and 113.17 nm, 121.11 nm, and 131.79 nm for 2%, 6%, and 10% Ti-doped CuS thin films, respectively. The optical bandgap of the films ranged between 2.40 eV and 2.60 eV. Structural analysis confirmed the hexagonal phase of CuS, with lattice constants a = b = 3.7920 Å and c = 16.3440 Å.





