Operational performance of a 8-MW scale grid integrated Wind Energy conversion system
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2024.v12.838Keywords:
Wind Data Analysis, Resource Estimation, Cluster Wind Farm, Performance indicators, Power Curve, Annual Energy outputAbstract
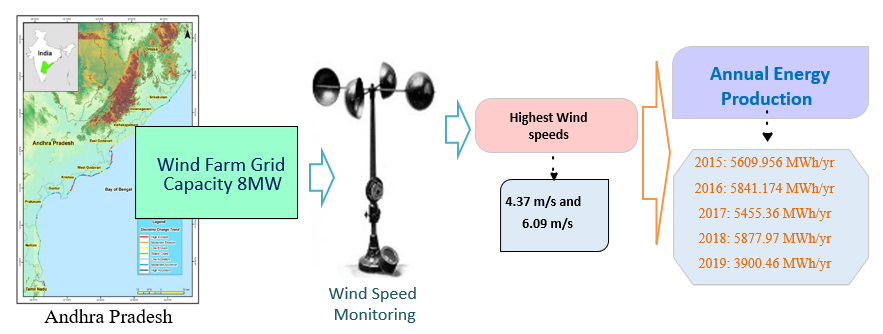
In this article, the operational performance of an 8 MW grid-connected cluster wind farm in Andhra Pradesh, India, is evaluated over a five-year period. At various heights above sea level, the wind farm's yearly average wind speeds were monitored. The highest recorded wind speeds were 4.37 m/s and 6.09 m/s. With capacity factors ranging from 24.6% to 44.9% between 2015 and 2019, the wind farm's reported annual energy production was found to be 5609.956, 5841.174, 5455.36, 5877.97, and 3900.46 MWh/yr. About 21.68% of the total wind farm was available. Analysis of the mean bias error (MBE) and normalized mean bias error (NMBE), which is the normalized version of the MBE, indicated significant trends between 2015 and 2019 in this study. The case study suggests building the right turbines nearby the research region to enhance the performance of wind farms.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.838
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2024 P. Venkata Sireesha, T. Sandhya

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission







