Five level modified CHB D-STATCOM for harmonic mitigation of EV charging station
Keywords:
Power quality, Harmonics, Cascaded H-bridge, DSTATCOM, DQ theoryAbstract
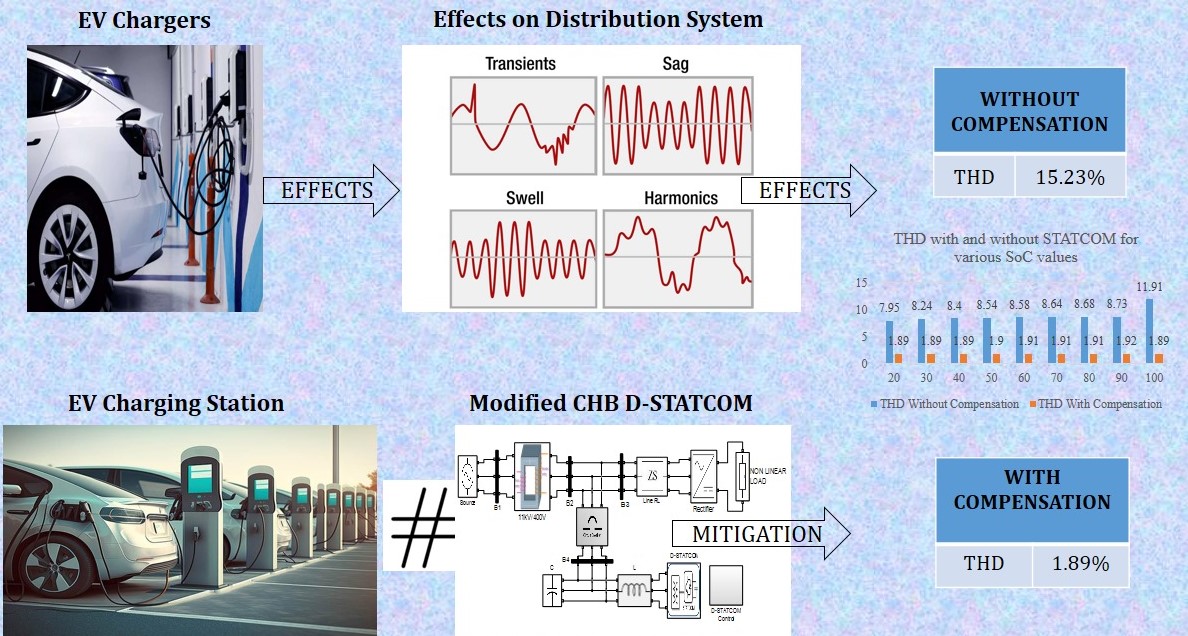
An electric vehicle (EV) charging station can be considered a non-linear load because it typically uses power electronics in the forms of rectifiers or inverters to form the necessary interface required for EV charging. These power electronics devices introduce nonlinearities in the current draw from the grid. Non-linear loads draw non-sinusoidal current thus resulting in harmonics. In the case of an EV charging station, the power electronics devices can cause harmonic distortion due to their switching action. This harmonic distortion can affect the power quality of the electrical system. The STATCOM (Static Synchronous Compensator) is an emerging solution for mitigating harmonics. Multilevel converters have found extensive utilization in STATCOM applications due to their capacity to enhance the compensator's power rating, rendering it appropriate for medium or high-voltage situations requiring substantial power output. This results in improved efficiency and reduced electromagnetic interference. The modified cascaded H-bridge topology of multilevel inverters allows for increased voltage levels and reduced harmonic distortion, while the DQ theory provides a robust and efficient control strategy. This paper presents a five level modified cascaded H-bridge (MCHB) D-STATCOM controlled with SRF theory to improve harmonic profile of the EV charging station. The performance is evaluated through MATLAB/Simulink simulation and the results show its effectiveness in improving power quality under different operating conditions. The proposed system offers several advantages over existing approaches, including increased voltage levels, reduced harmonic distortion, and improved control performance.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.738
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Prashant Magadum, Sangamesh G Sakri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



