Detection of Familiar and Unfamiliar faces from EEG
Keywords:
Face perception, ICA decomposition, EEGLAB (MATLAB extension), SPA, independent T-test, Medical signal processingAbstract
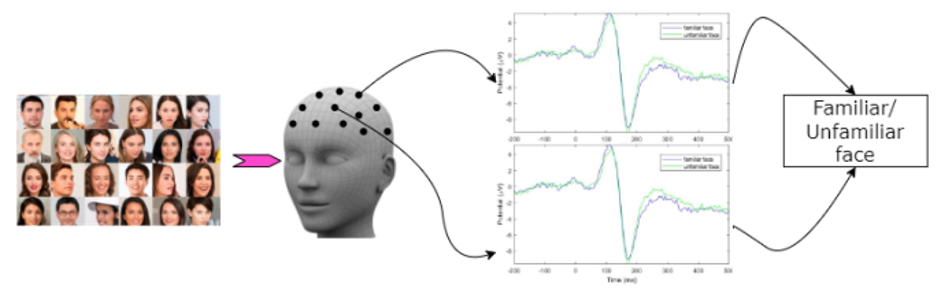
Face recognition is a complex cognitive task that involves a distributed network of neural sources. While some components of this network have been identified, the temporal sequence of these components is not well understood yet. This study contains the detection of familiar or unfamiliar faces by using the event-related potential (ERP) response from the recorded EEG signal from subjects when they were introduced to stimulus as familiar faces, unfamiliar faces and scrambled faces, this study includes the dataset which contain the EEG data from 18 subjects for face recognition task, this recorded data is being used to detect if there is any significant difference recorded EEG data for type of faces. ERP artifacts based on the variance of components decomposed by PCA, the results achieved by using ICA and SPA then compared with each other to make the exact and accurate decision on the EEG response for a familiar face and unfamiliar faces.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.715
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Navin Vanzara, Chintan P. Shah, Avani Vithalani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



