Modelling EEG Signal using multivariate denoising and design of the optimized CSP filter for efficient feature extraction applicable in non-invasive BCI
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2024.v12.814Keywords:
Multivariate, Common Spatial Pattern (CSP), Brain Computer Interface(BCI), Electroencephalogram (EEG)Abstract
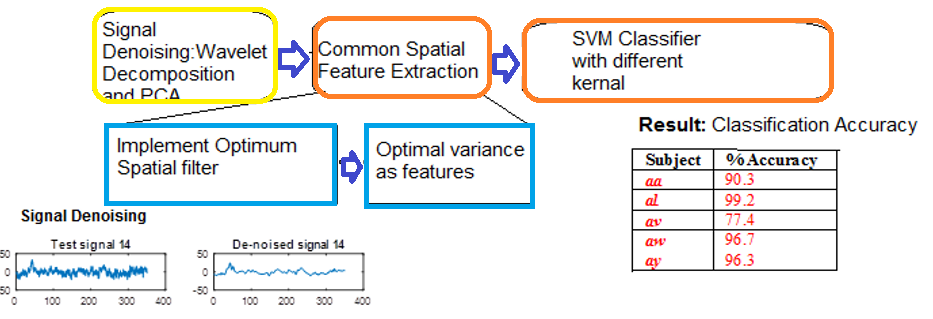
Electroencephalographic (EEG) signals corresponding to motor imagery (MI) are efficient input to the brain-computer interface (BCI), but are highly contaminated and have a spatial distribution of the activity related variation. This work proposes a filtering method having the combined advantage of wavelet transform and principal component analysis (PCA) for pre-processing of the signal. Transform domain helps to capture the main features of the signals using matching wavelet function while PCA reduces the feature dimension. Correlation structure of noise used here helps in cancelling interferences and to rebuild the signal. Optimized and subject-specific common spatial pattern (CSP) filter design is proposed for extracting the features. Empirical analysis of number of electrodes for building the CSP filter mask leads to selection of 21 electrodes from MI region gives the best performance. The method executes weighing of the electrodes and accordingly assigning the importance to the electrode while forming the filter. Filter induced optimized variance of the signals acts as the features for two-class support vector machine (SVM). Classification accuracy (CA) obtained for subject aa is 90.3%, and for subject al it is 99.2%. Subject aw having small training set gives accuracy to be 96.7% whereas for subject ay it is 96.3%.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.814
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Vrushali G. Raut, Sandhya A. Shirsat, Rohita P. Patil, Omkrakash S. Rajankar, Supriya O. Rajankar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission







