DNA-protein crosslinks are key to platinum-based chemotherapeutic cytotoxicity
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.cbl.2024.v11.663Keywords:
Platinum-based chemotherapeutics, DNA damage, Interstrand crosslinks, Lethal Dose, protein damage, cancer therapeutics, cytotoxicity, DNA-protein crosslinksAbstract
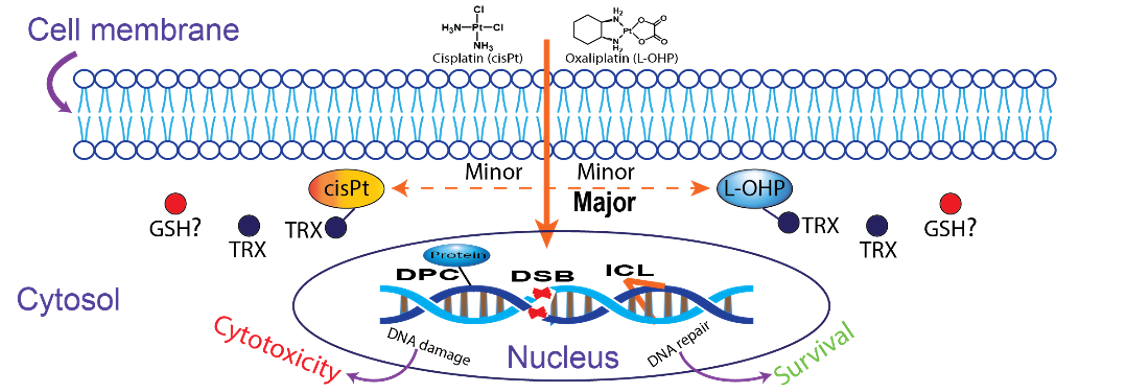
Platinum-based chemotherapeutics inflict a spectrum of DNA damage, including DNA adducts, DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs), and interstrand crosslinks (ICLs) to variable extents. These diverse lesions may contribute to the overall toxicity of these therapeutic agents. Nonetheless, a gap exists in comparative studies elucidating the specific DNA damage responsible for their toxicity. Therefore, we exposed MRC5SV cells to equitoxic doses (LD10) of cisplatin (cisPt) and oxaliplatin (L-OHP) and systematically examined the induction of DPCs, ICL, and protein damage. Our findings suggest that DPCs emerge as the crucial cytotoxic DNA damage for both cisPt and L-OHP, highlighting their central role in the mechanism of action driving the cytotoxicity of platinum-based therapeutics. Both drugs show induction of ICLs as computed by the unique sensitivity of Fanconi anemia cells to the drugs. Additionally, both cisPt and L-OHP didn’t show protein damage as indicated by the absence of TRX1 oxidation post-treatment. Overall, our results underscore the critical involvement of DPCs in the toxicity of platinum-based drugs, emphasizing the importance of DPCs as potential cancer therapeutic targets.
URN:NBN:sciencein.cbl.2024.v11.663







