Beneficial impacts of Astaxanthin on Biomarkers of Antioxidant status and oxidative damage in Rats exposed to Ambient air
Abstract
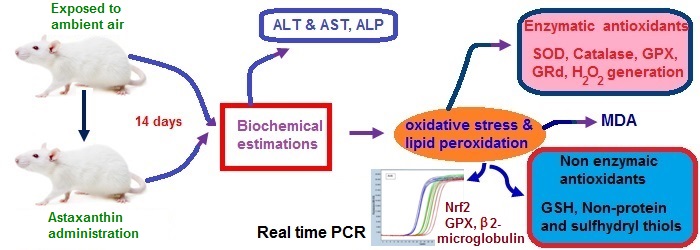
Effect of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis on lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress induced by ambient air exposure was studied. Wistar albino rats were exposed to ambient air was administered with astaxanthin in doses varying between 0.5 to 2% of food intake. Various biological parameters like ALT, AST, ALP, malondialdehyde, hydrogen peroxide, superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione reductase, were estimated biochemically and the expression of Nrf2 and glutathione peroxidase genes were estimated by reverse transcriptase PCR. Plasma ALT, AST, ALP, MDA and the activity of antioxidant enzymes; SOD, GRd, catalase were found increased significantly in ambient air exposed rats. Ambient air exposure decreased the levels of glutathione, non protein thiols and GPx expression whereas total thiols and expression of Nrf2 increased. However the concurrent administration of astaxanthin was found to reverse these changes in a dose dependent manner. The results of this study revealed the ability of astaxanthin to alleviate liver toxicity and oxidative stress induced by ambient air exposure and points to the possibility of developing astaxanthin as a dietary supplement that reduce the ill effect of toxic chemicals from ambient air.



