Design, synthesis and biological activity evaluation of Carboxylic acid derivatives of substituted 2,3-Diphenyl-2H-1-Benzopyrans as novel selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators
Abstract
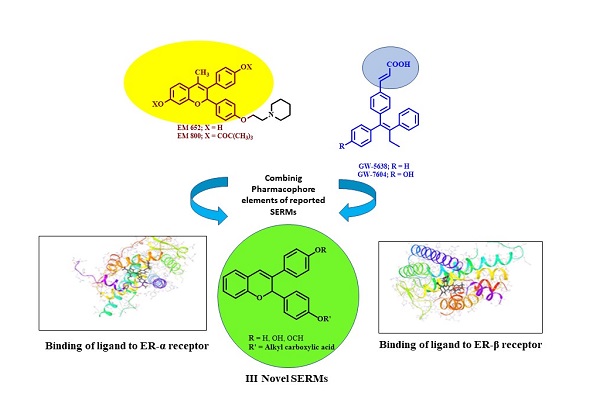
Synthesis of the molecules that can interact with estrogen receptors (ERs) which show precise manifestation of efficient applications in selective tissue, termed as selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) are of great medicinal significance today. With the problems associated with the selectivity and efficacy of the prevalent estrogen dependent anticancer drugs, the effort continues to evolve more effective SERM compounds. This paper describes the synthesis, biological evaluation and computational studies of a series of novel benzopyrans (I-III) to facilitate research in this direction. The evaluation studies revealed that the novel benzopyran analogues exhibit significant antiestrogenic activity when studied on male/female rats of Sprague-Dawley strain and better safety profile on uterus than the most prevalent antibreast cancer drug Tamoxifen. The results demonstrate that the series could produce compounds of alternate therapeutic regimes similar to that of the novel reported compounds of proven prevalent anticancer activities.



