Characterization and evaluation of biological and photocatalytic activities of selenium nanoparticles synthesized using yeast fermented broth
Keywords:
Selenium nanoparticles, antibacterial, anti-proliferative, antioxidant, Photocatalytic degradationAbstract
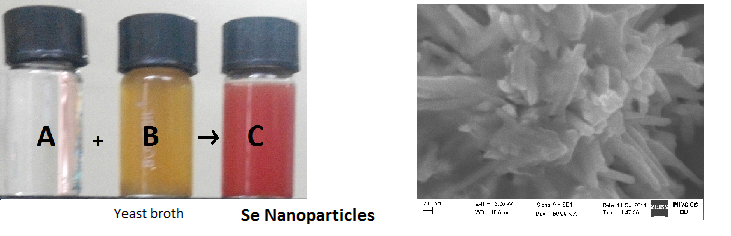
The present article reports an environmentally benign and unexploited method of green synthesis of selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) using an agro-waste based yeast fermented broth as a reducing agent. Treatment of aqueous solution of Na2SeO4 with agro-waste based yeast fermented broth yielded stable selenium nanoparticles. The UV-Visible spectroscopy of nanoparticle solution showed absorption maxima at 540nm. SEM observations revealed the predominance of 170–240nm rod shaped particles arranged as “flower-like” crystalline aggregates. SeNPs showed potent antibacterial activity against common biofilm-forming Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus and significant anti-proliferative activity against A549, MCF7, and SKOV3 (cancer) cell lines. The SeNPs exhibited a concentration dependent increase in antioxidant activity. Further, the green-synthesized SeNPs have also been tested as photocatalyts for degradation of methylene blue (model dye), under visible light illumination at room temperature and the rate of degradation has been studied spectrophotometrically.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2016 ScienceIn Publishing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

