Comparative studies of anticancer and antimicrobial potential of bioinspired silver and silver-selenium nanoparticles
Keywords:
Anticancer, Antimicrobial, Silver nanoparticles, Plant extractAbstract
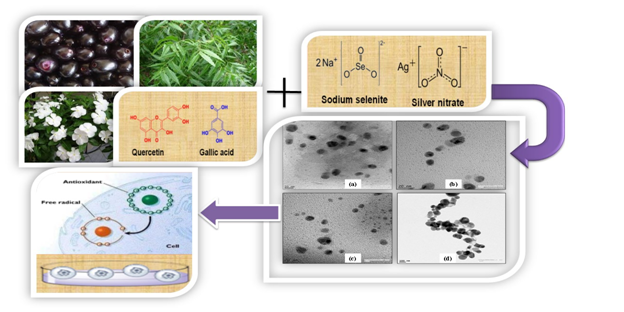
The antimicrobial and anticancer potential of synthesized silver nanoparticles by various medicinal plants and silver-selenium nanoparticles by phytochemicals (quercetin and gallic acid) are reported here. Medicinal plants such as Syzygium cumini, Azadirachta indica and Catharanthusroseus and quercetin-gallic acid as phytochemicals were selected after screening of various plants and phytochemicals in terms of the ability of nanoparticle synthesis. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized using various analytical instrumentation techniques. All the nanoparticles are having less than 40 nm in size as confirmed by electron microscopy. Bactericidal action of the nanoparticles was determined using broth microdilution method on two microbial strains (Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis). The results specified that all types of nanoparticles exhibited comparable bactericidal action against the different strains at 100 µg/ml, when compared to the standard drug, chloramphenicol (50 µg/ml). Additionally, the anticancer potential of the nanoparticles was evaluated using MTT assay on various cancer cells (HeLa, Hek-293 and MCF-7). The results concluded that Syzygium cumini silver nanoparticles were highly active at the minimum concentration of 10 µg/mL against all type of cells. The synthesized nanoparticles destroy the bacterial and tumour cells in a dose-dependent manner.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2016 ScienceIn Publishing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

