User Location prediction using Hybrid BIRCH clustering and Machine Learning approach
Keywords:
User Location, Trajectory, Clustering, Machine LearningAbstract
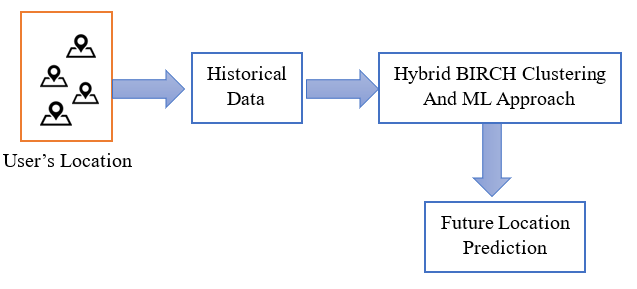
This paper discusses the importance of location prediction using machine learning methods and its potential applications in various fields. The accuracy of these models is high, but they face challenges such as data quality, model complexity, privacy concerns, and limited data availability. Despite these challenges, the future scope of location prediction is vast, and ML techniques play a crucial role in improving these models. The paper sheds light on modern techniques for better performance and highlights the difficulty of predicting a user's position in real-time, which limits the utility of location-based services. This study proposes a novel approach for predicting complete user trajectories using a Balanced Iterative Reducing and Clustering using Hierarchies (BIRCH) , based on a scalable architecture that uses clustering to reduce the search space. Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (BiLSTM) with random forest classifier models are used for analyzing temporal data and predicting trajectories. The proposed approach, termed BIRCH-LSTM, outperforms other reported results on prediction accuracy. The result analysis of the proposed solution has potential applications in navigation systems, traffic management, and location-based recommendation systems.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.701
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Madhur Arora, Sanjay Agrawal, Ravindra Patel

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



