Identification and characterization of Microbial Consortia present in sewage samples collected from Sewage Treatment Plant, Jaipur, (Raj.)
Keywords:
Biological Oxygen Demand, sewage analysis, wastewater management, water pollution, environmental scienceAbstract
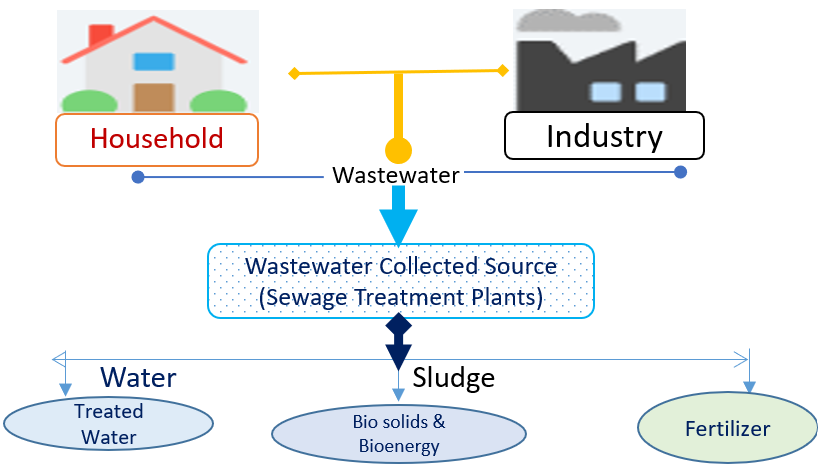
Conventional wastewater management methods utilizing the municipal and industrial waste water in a strict aerobic conditions are quite expensive in terms of consumption of excess amount of energy and available resources which consciously results in creation of big quantity of secondary sludge mostly containing many of the toxic pollutants. On this panorama several physico-chemical parameters can act as validation marker to estimate the amount of bioremediation and clearance out of pollutants within the sewage treatment plants. The present study demonstrated the identification of available microbial consortia along with the estimation of several physico-chemical parameters for the Sewage samples, collected from sewage treatment plant. The study showed the presence of specific microbes such as Salmonella Spp., Escherichia Spp., Pseudomonas Spp., Alcaligens Spp., Staphylococcus Spp., Streptococcus Spp., etc. in the sludge samples and Salmonella Spp., Bacillus Spp., Escherichia Spp., Staphylococcus Spp., etc. in the waste water sample. Moreover, it also validated the efficiency of microbial fuel cells within the sewage plant; as samples collected from different chamber compartments have showed significant reduction in many physico-chemical parameters such as BOD, COD, hardness, Organic carbon, Nitrate, etc.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2023.v11.516
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ankita Saxena, Varsha Gupta, Sonika Saxena

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission



