Machine translation of low resource Indian language using deep learning approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2025.v13.1127Keywords:
Neural Network, Machine Translation, sparse occurences, Bahdanau Attention MechanismAbstract
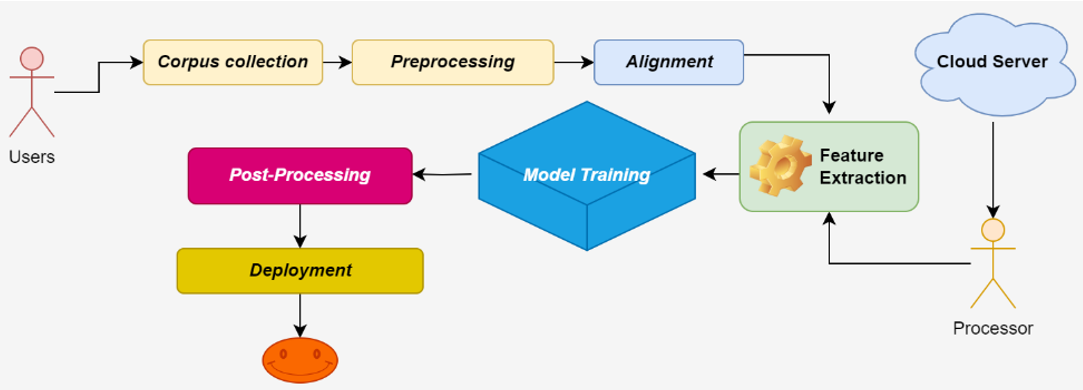
The creation of an English-to-Bhojpuri machine translation (MT) system is presented in this paper, with an emphasis on the difficulties in translating words based on Devanagari script. Due to the sparse occurrence of distinct Devanagari words and the lack of training data, accurate translation is challenging in Bhojpuri, a language spoken in Bihar, India. A sequence-to-sequence model trained on a self-made dataset of 10,105 English-Bhojpuri sentence pairs is used to construct the system. Particular focus is placed on adding examples of these distinct words to the dataset. The model uses word embeddings and attention mechanisms to capture the semantic and contextual relationships required for precise translation. This machine translation (MT) system provides a customized solution for handling Indian languages in the Devanagari script by tackling the linguistic complexities of Devanagari words, improving the accuracy and fluency of English-to-Bhojpuri translation.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Madhuri Tayal, Aniket Tiwari, Anuj Dharme, Pratik K Agrawal, Animesh Tayal, Nilima V. Pardakhe

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission







