Contemporary advances in therapeutic portfolio of 2-Azetidinones
Abstract
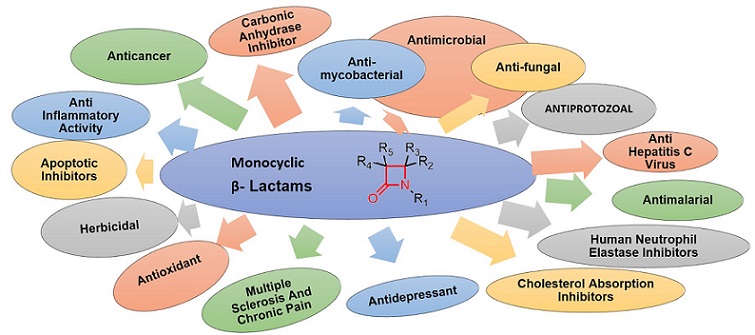
The heterocycle moieties form the site of reaction in many enzymes and co-enzymes and also act as an important pharmacophore in the pharmaceutical drug designs. 2-Azetidinones are the 2-carbonyl derivatives of azetidine, more commonly known as ?-lactams. These structural entities occupied a central role in the vigil against bacterial infections over the past few decades. A subclass of these heterocyclic systems, monobactams or monocyclic ?-lactam derivatives exhibits several biological activities including antibacterial, antifungal, antiprotozoal, anti-mycobacterial, anti-HIV, antiviral, antimalarial, antioxidant, apoptotic inhibitors, anti-inflammatory activity, anticancer activity, herbicidal activity, etc. Monobactams has resistant to the ?-lactamase enzyme and could be a reasonable starting point for developing new drugs or inhibitors. In the present review, pharmacological activities of monocyclic ?-lactam derivatives have been discussed with respect to current research in the structure-activity relationships in different therapeutic areas.



