Digital sensors for detecting toxic gas leaks
Keywords:
Gas sensors, pulsating sensor, transduction technique, logic gate oscillatorAbstract
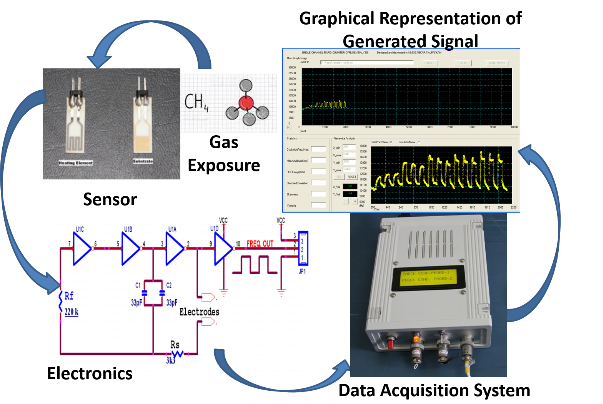
Design of an innovative gas sensor with direct digital signal output is presented in this paper. These sensors are suitable for diverse field applications envisaging detection of leaks of gases such as methane, hydrogen, ammonia and other toxic gases. They are also used in stand-alone gas monitoring systems in chemical industries. The sensor probe consists of gold inter-digitated electrodes sputtered on insulating substrate. A heater element made up of platinum meander structure is on the other side of the substrate, which is used to assess the performance of the sensor at different temperatures. The gold electrode is connected with a fixed value capacitor as timing circuit of a logic gate oscillator (LGO). In presence of the gas, the resistance change across the sensing electrodes at constant temperature is measured as frequency change of digital pulse output from the LGO circuit. This transduction method works with 5V DC voltage and generates Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) compatible digital pulse output. Hence it reduces complexity of signal generation hardware by eliminating use of amplifier and filter circuits. The frequency of TTL pulse signal output in response to the change in resistance induced by gas is calibrated for different concentrations and heater voltages. The performance of the gas sensor was studied at various temperatures and the optimum temperature for maximum sensitivity was found to be around 100°C. The precision, sensitivity and the lowest detection limit in measurement of methane gas using this method are <100 ppm, approx. 10 Hz/ppm and approx. 100 ppm, respectively.

