Preparation, characterization and in-vitro drug release evaluation of Ganciclovir loaded Chitosan nanoparticles
Keywords:
Ionic gelation, Drug Release, Particle Size, Drug delivery, nanomedicine, nanobiotechnologyAbstract
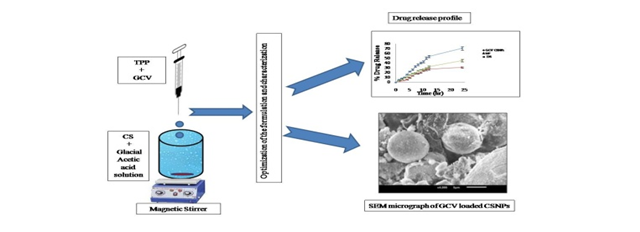
Chitosan Nanoparticles (CSNPs), as drug carrier, can be utilized for enhancing permeability of poorly absorbed drugs. The aim of this work was to enhance the permeability of Ganciclovir (GCV) by loading into CSNPs. An ionic gelation method was undertaken to develop GCV loaded CSNPs. Several process and formulation parameters were screened and optimized through 25-2 fractional factorial design and Box-Behnken design respectively. The CSNPs were evaluated and characterized for their particle size and shape, surface charge, entrapment efficiency, crosslinking mechanism (dried CSNPs) and drug release study. The optimized CSNPs were found with particle size of 121.20 ± 2.7 and entrapment efficiency (% EE) of 85.15 ± 1.1%. Transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy and dynamic light scattering technique revealed spherical particles with uniform size. The in-vitro release profile was found to be sustained up to 24 hr. Thus, incorporation of GCV into CSNPs results in enhanced permeability, that may in turn increase overall oral absorption of the drug.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2016 ScienceIn Publishing

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.

