Delta arsenene nanoribbon as a sensing element towards phenol and benzene vapours – a first- principles insight
Keywords:
Arsenene, Nanoribbon, Physisorption, Sensor, Benzene vapour, Phenol vapour, vapour sensorAbstract
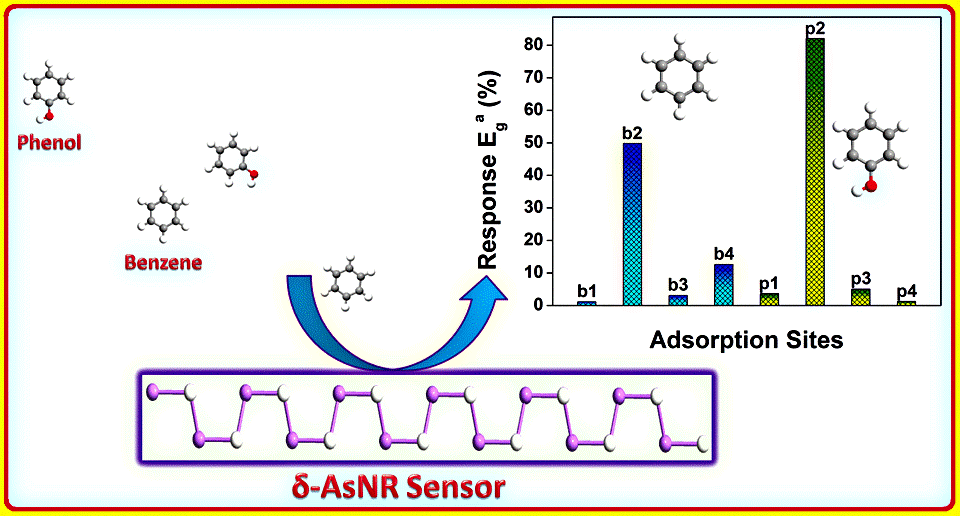
The advancement in the nanomaterials opens the gate for various sensing substrates towards gas/vapours. In the current work, delta arsenene nanoribbon (δ-AsNR) is used as adsorbing element towards phenol and benzene vapours. The formation energy of δ-AsNR is recorded as -4.117 eV/atom confirming the stable structural geometry. The band gap of bare δ -AsNR is calculated to be 1.368 eV in GGA/B86LYP level of theory. Furthermore, the adsorption of phenol and benzene vapours on δ-AsNR exhibits physisorption with exothermic nature of adsorption. The charge transfer reveals that phenol and benzene molecules resemble donor and δ-AsNR as acceptor of electrons. Besides, the projected density of states and band structure variation are noticed owing to adsorption of phenol and benzene molecules on δ -AsNR. Hence, it is evident that δ -AsNR is one of the base substrate to sense the presence of phenol and benzene vapours in the environment.

