Deep Learning approach for Co-operative Spectrum Sensing under Congested Cognitive IoT networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.jist.2024.v12.778Keywords:
Cognitive Radio, Spectrum Sensing, Machine Learning, Cooperative Spectrum Sensing, IoT NetworksAbstract
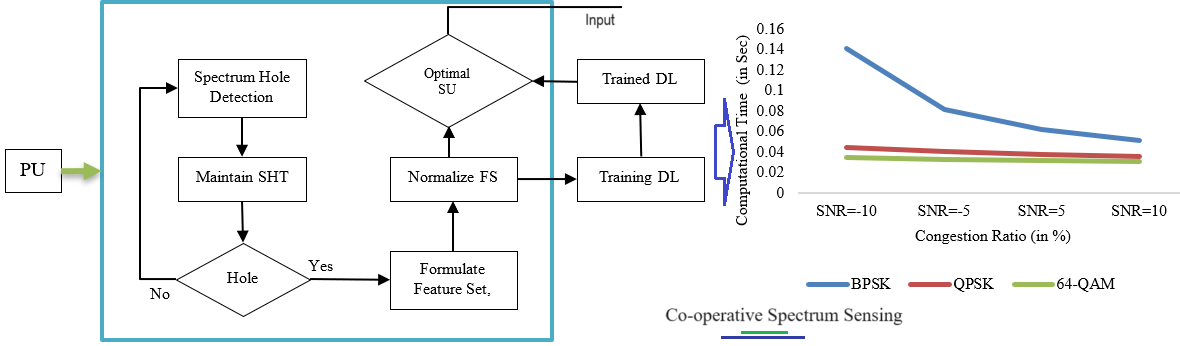
Cognitive radio technology enables intelligent wireless communication systems to learn from their surroundings, allowing secondary users to reuse available radio resources while avoiding interference with licensed users. Spectrum sensing is a critical component, and machine learning approaches are gaining interest for improving performance and predicting spectrum availability. Supporting multiple secondary users simultaneously enhances spectrum sensing speed and data transfer efficiency. The research's second phase introduces a hybrid learning algorithm for Cooperative Spectrum Sensing in congested Cognitive IoT Networks. It evaluates the performance of BPSK, QPSK, and 64-QAM modulation schemes under varying Signal-to-Noise Ratios (SNRs) in a simulated network environment. The hybrid model, incorporating ResNet-50 architecture, adapts to network congestion levels, providing insights for optimizing digital communication systems in diverse congestion scenarios.
URN:NBN:sciencein.jist.2024.v12.778
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Yogesh Mishra, Virendra S. Chaudhary

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Rights and Permission







