Early manifestation of hyperuricemia and its pathophysiological interface with adiposopathy and metabolic syndrome among young adult: Cross-sectional study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.cbl.2024.v11.653Keywords:
Body mass index, Central obesity, hyperuricemia, Metabolic SyndromeAbstract
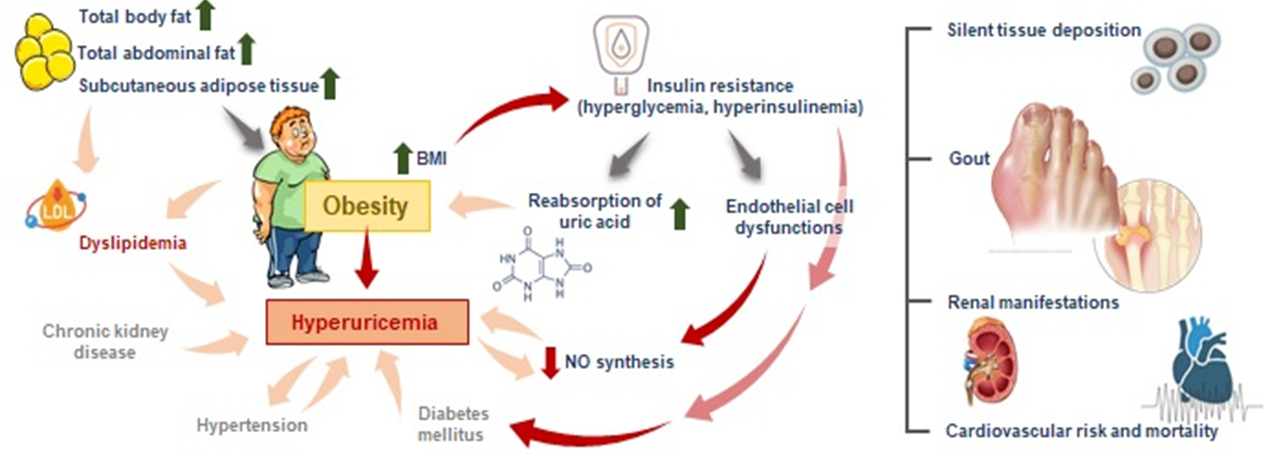
The association between serum uric acid (SUA) levels and visceral adipose tissue, subcutaneous adipose tissue, and metabolic syndrome (MetS) in young, healthy subjects warrants scientific investigation. In this cross-sectional research involving 114 subjects, various anthropometric parameters, such as body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and skinfold measurements were measured. Additionally, fasting blood glucose (FBG), SUA concentrations, lipid profiles, and blood pressure were assessed. Mathematical models estimated body fat percentage (BF), total abdominal fat (TAF), intra-abdominal adipose tissue (IAAT), and subcutaneous adipose tissue (SCAT). SUA concentrations were categorized into quartiles: Q1 ≥3.04 mg/dl, Q2 3.05-3.86 mg/dl, Q3 3.89-4.67 mg/dl, and Q4 4.68-7.87 mg/dl. MetS was delineated using the criteria from the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III. Statistical methodologies comprised t-tests, one-way ANOVA, and Pearson's correlation. The incidence rates for MetS, hyperuricemia, and hypertriglyceridemia were 11.4%, 5.26%, and 27.19%, respectively. Abdominal obesity, based on WC, was 19.3%. Males showed a more pronounced increase in IAAT (26.23%) than females (13.20%), leading to a total prevalence of 20.18%. The total SCAT incidence was 21.93%, with females (21.53%) outnumbering males (19.67%). The incidence of elevated FBG was 21.93%, suggesting a pre-diabetic condition. Hypertension rates, represented by systolic and diastolic blood pressures, were 3.51% and 15.79% respectively. Metabolic irregularities escalated with increasing SUA levels. The data indicate that young adults manifesting MetS components often exhibit elevated SUA concentrations, proposing that SUA might be an added MetS factor.
URN:NBN:sciencein.cbl.2024.v11.653







