Characterization of podophyllotoxin biosynthetic pathway and future prospect of podophyllotoxin production from Podophyllum hexandrum Royle
Abstract
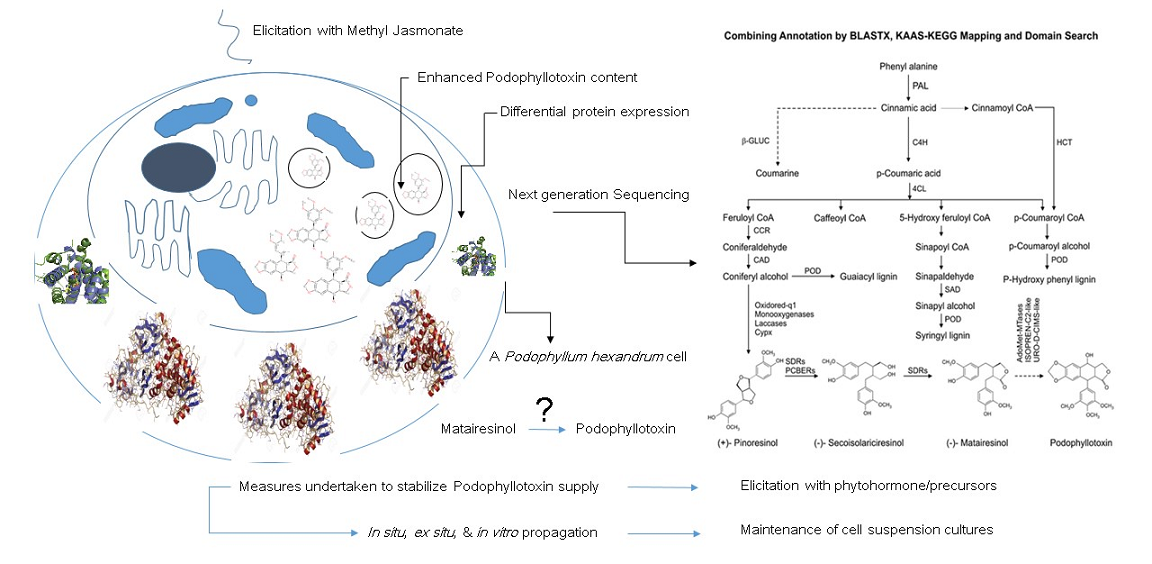
Podophyllotoxin (PTOX), a cytotoxic lignan with immense anticancer and other therapeutic properties, is primarily obtained from the roots and rhizomes of Podophyllum hexandrum and P. peltatum. In view of its current shortage of commercial supply, alternative strategies have long been on the look out. Recent works, including ours, are presently concentrating to dissect the downstream PTOX pathway genes, which could open vents to the metabolic engineering of the PTOX pathway in extensively studied and standardized hosts. This review exclusively deals with the characterization of PTOX pathway and explore the possibilities to stabilize PTOX supply from P. hexandrum, a native of the Indian alpine region. Here, we discuss the hypothetical PTOX pathway and the use of newer NGS technology to unravel probable important target transcripts of the downstream PTOX pathway. Additionally, we have elucidated the measures adopted in the last three decades to find realistic solutions to the shortage in supply of industrial PTOX.



