Beyond Ethylene Oxide (EtO): A comprehensive review of sustainable sterilization technologies for medical devices
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.62110/sciencein.btl.2025.v12.1161Keywords:
Radiation, Ethylene Oxide , Sterilization, Carcinogenicity, Biomaterials, MicrowaveAbstract
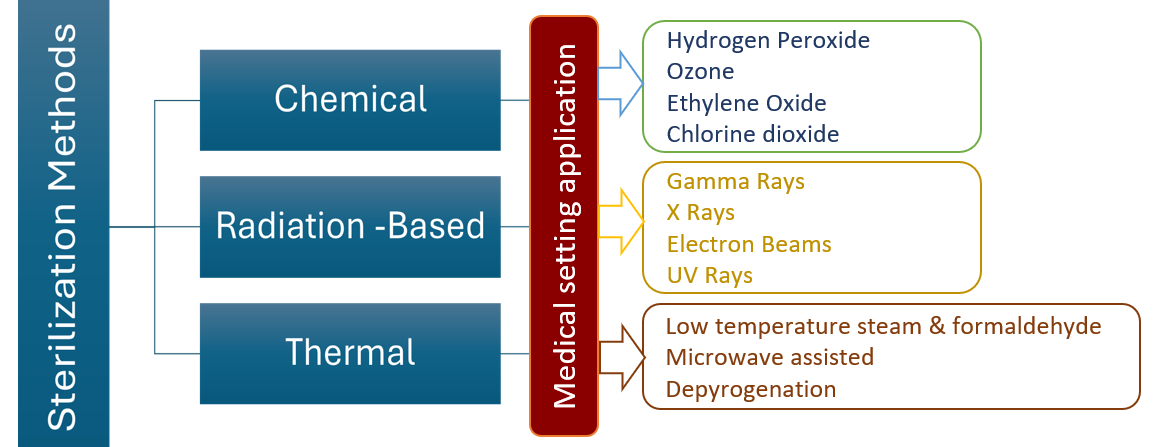
Ethylene oxide (ETO) sterilization is recognized as a key method for eliminating bacteria in medical devices, especially those with electronic components, due to its compatibility with various materials. Despite its effectiveness, concerns about its environmental impact and risks to workers have prompted exploration of alternative sterilization techniques. This review systematically evaluates the challenges of ETO sterilization and explores other methods such as gamma irradiation, electron beam sterilization, hydrogen peroxide plasma, ozone, steam autoclave, supercritical CO2, cold plasma, UV light, and pulsed light sterilization. Each technique is assessed based on factors like operation, performance, material compatibility, toxicity, and justification for use. The analysis provides a comparative evaluation of the methods, considering aspects such as cycle time, cost, scalability, penetration depth, and process complexity. It highlights the barriers to transitioning away from ETO and discusses alternatives that could replace it. The article aims to guide healthcare professionals, manufacturers, and researchers in selecting suitable sterilization methods for medical devices and biomaterials. Overall, it underscores the importance of finding safer, environmentally friendly alternatives to ETO to improve patient safety, enhance product quality, and reduce environmental impact in medical device sterilization.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Aricson Pereira, Gowtham Nakka, Sakshi Gupta

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





