p-Co3O4 supported heterojunction Carbon Nanofibers for Ammonia gas sensor applications
Keywords:
Carbon Nanofibers, sensing mechanism, Gas Sensing, Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS), metal oxideAbstract
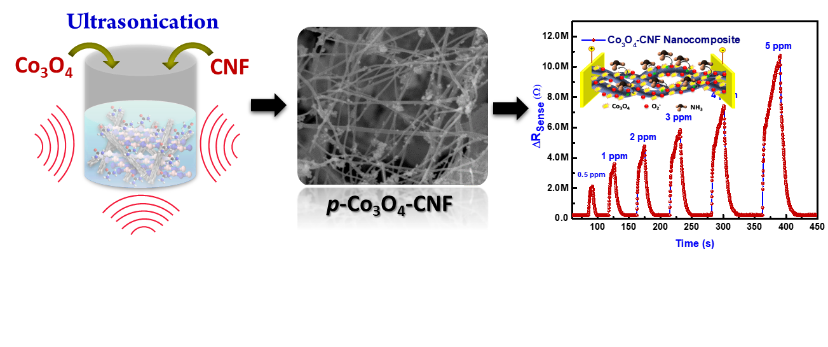
Trace level detection of gaseous ammonia is extremely important both in terms of environmental monitoring as well as health monitoring sectors. Metal oxide semiconductor, p-Co3O4 based nanostructures have been extensively used as gas sensing materials for the detection of a wide range of toxic gases. However, the pristine p-Co3O4 based sensors always face poor sensitivity and selectivity towards target gases. In order to enhance the sensitivity and selectivity of p-Co3O4 based sensors, carbon nanofibers can be utilized to create heterojunctions for boosting conductivity and rapid response. Herein, we report the synthesis and characterization of NH3 gas sensor properties of p-Co3O4 supported heterojunction carbon nanofibers (CNF) for the detection of trace level concentration of NH3. Structural and morphological analyses have been carried out using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman and Field-Emission Scanning Electron microscope (FE-SEM), etc. The evaluation of gas sensing properties of p-Co3O4 supported CNF nanostructures was performed, which exhibited high sensitivity for detecting NH3 at lower working temperature and its complex sensing mechanism has been discussed. This investigation can pave the way to novel strategies for designing and fabricating low-cost, high performance NH3 gas sensors application.

