HCN adsorption on Phosphorus-doped MoS2 monolayer: First principles calculations
Keywords:
HCN adsorption, P-MoS2 monolayer, Gas sensingAbstract
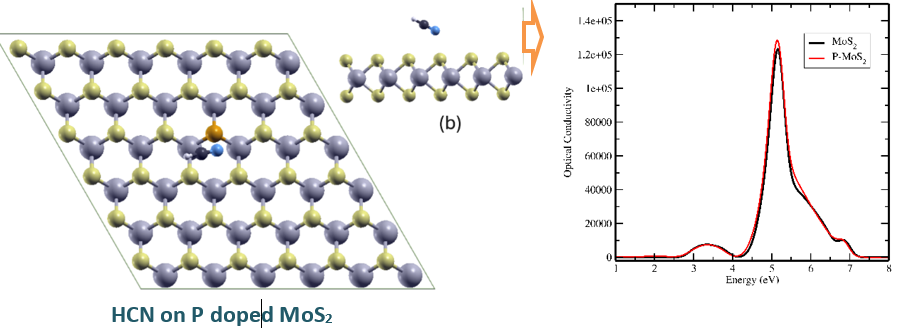
In this study, we examine the possibility of using MoS2 monolayers doped with phosphorus atoms as a sensor for hydrogen cyanide (HCN) gas by making use of density functional theory (DFT), employed with the SIESTA code. MoS2 has shown great potential in nanoelectronics and sensing because of its distinct electronic characteristics, particularly in its monolayer state. Identifying HCN is essential for ensuring safety and monitoring the environment, which drives the search for new materials for sensing purposes. It is believed that doping MoS2 monolayers could improve their ability to detect HCN by altering its electronic configuration. This document presents our theoretical background and anticipated results. By investigating the capabilities of phosphorus-doped MoS2 monolayers as gas sensors, this study seeks to advance the development of sensor technologies and their use in detecting hazardous gases.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Issue
Section
URN
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Neeraj Thakur (Author); Tamanna, Arun Kumar (Translator); Amarjeet Singh (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
